GOST 19831-74
Group G23
STATE STANDARD OF THE UNION OF THE SSR
TAPS FOR TRAPEZOIDAL THREAD
Thread tolerances
Taps dies trapezoidal thread. Tolerances on thread
Valid from 01.01.75
until 01.01.80*
_______________________________
* Expiry date removed
Decree of the State Standard of the USSR of December 10, 1980 N 5705.
(IUS N 2, 1981). - Note "CODE".
DEVELOPED by the All-Union Scientific Research Instrumental Institute (VNII)
And about. director Tsvis Yu.V.
Head of the theme Pudov V.M.
Artist Dubinskaya G.Ya.
INTRODUCED by the Ministry of Machine Tool and Tool Industry
Member of the Board Trefilov V.A.
PREPARED FOR APPROVAL by the All-Union Research Institute for Normalization in Mechanical Engineering (VNIINMASH)
Director Verchenko V.R.
APPROVED AND INTRODUCED BY Decree of the State Committee for Standards of the Council of Ministers of the USSR dated May 24, 1974 N 1296
1. This standard applies to taps for trapezoidal threads in accordance with GOST 9484-73 *.
_________________
* GOST 9484-81 is valid. - Note "CODE".
2. Taps must be manufactured with degrees of accuracy H5 and H6.
3. The maximum deviations of the thread of the taps must correspond to those indicated in the drawing and in the table.
Nomi- | Thread pitch, mm | Limit deviations, microns | Pre- |
||||||||
outside diameter | medium diameter | internal | thread pitch | ||||||||
on a length of 25 mm | |||||||||||
Over 5.6 to 11.2 | |||||||||||
Over 11.2 to 22.4 | |||||||||||
Over 22.4 to 45 | |||||||||||
Over 45 to 90 | |||||||||||
APPENDIX to GOST 19831-74
Reference
H5 precision taps ensure thread accuracy 7 H, taps of accuracy degree H6 - accuracy of the thread being cut 8 H.
The specified thread accuracy can be obtained by using taps on machines that meet the accuracy standards imposed on them, using chucks that provide self-alignment of taps in the radial direction and compensate for misalignment of the hole and tap.
The text of the document is verified by:
official publication
M.: Publishing house of standards, 1974
Profiles and thread sizes
(GOST 9484-81)The standard applies to trapezoidal threads and establishes the profiles and dimensions of its elements.
MAIN PROFILE

Example symbol trapezoidal single-start thread with a nominal diameter of 20 mm, a pitch of 4 mm and a tolerance field of an average diameter of 7e:
Tg 20 x 4 -7e
NOMINAL PROFILES
external and internal thread

h 3 - height of the external thread profile; H 4 - the height of the profile of the internal thread; d 3 - inner diameter of the external thread; D 4 - outer diameter of the internal thread; R 1 - rounding radius at the top of the external thread; R 2 - twisting radius in the cavity of the external and internal threads; a c - clearance at the top of the thread.
DIAMETERS AND PITCHES
trapezoidal single-start thread according to GOST 24737-81
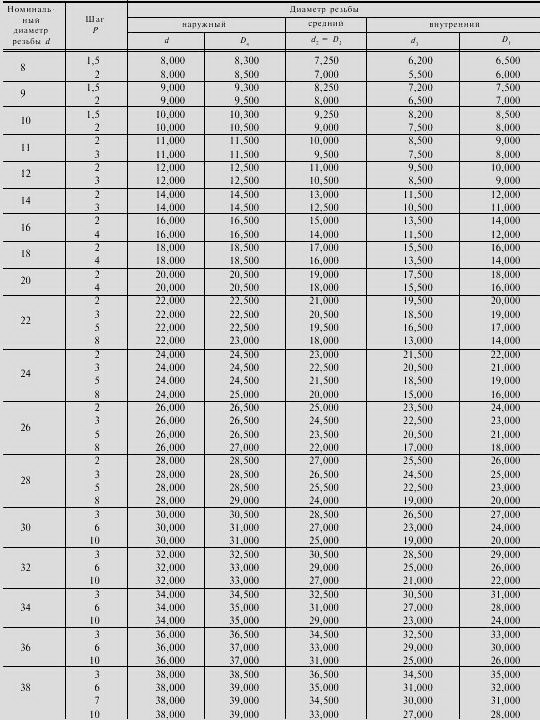




Preferred diameters and steps are specified in GOST 24738-81. Numerical values of tolerances of diameters and steps - according to GOST 9562-81
DIAMETERS AND PITCHES
trapezoidal multi-start thread according to GOST 24739-81



Notes:
1. Steps in a box are preferred.
2. The steps indicated in brackets are not recommended when developing new designs.
3. Threads, in which the stroke value is marked with *, have a lead angle of more than 10 o. For these threads, the deviation of the profile shape must be taken into account during production.
4. In technically and economically justified cases, it is allowed to use other values of nominal thread diameters in accordance with GOST 24738-81.
5. When choosing thread diameters, the first row should be preferred to the second.
An example of a symbol for a trapezoidal multi-start thread with a nominal diameter of 20 mm, a stroke value of 8 mm, a pitch of 4 mm and a tolerance field of 8e:
Tg 20-8 (P4) - 8e
Same, left:
Tg 20-8 (P4) LH - 8e
The make-up length, if different from the thread length, is indicated in millimeters at the end of the thread designation, for example:
Tg 20-8 (P4) LH - 8e - 180
Numerical values of the lengths of make-up related to groups N and L - according to GOST 9562-81.
Landing in a threaded connection is indicated by a fraction
Tg 20-8 (P4) LH - 8H / 8e - 180
The numerical values of the tolerances of diameters d and D 1 - according to GOST 9562-81.
The numerical values of the tolerances of diameters d 2, d 3 and D 2 - according to GOST 24739-81.
Trapezoidal Thread Application

The trapezoidal screw thread is a leading thread with a relatively large friction force, it is self-braking. The advantage for lifting technologies is that it does not require additional fixation in the rest position.
Trapezoidal thread is used to convert rotary motion into linear motion and is used primarily for rectilinear motion. It also finds its use as a lead screw in lathes or as a drive thread for the screw press of tables or vehicle bridges.
Application examples for trapezoidal spindle threads:
Feed movement on machine tools (e.g. adjusting and lead screws);
- movement on the manipulator;
- regulation of movement on lifting mechanisms and forklift trucks;
- movement of the shutter when locking injection molding machines;
- moving movement on assembly containers;
- vertical movement when working with a press.
Related Documents:
GOST 3469-91: Microscopes. Thread for lenses. Dimensions
GOST 4608-81: Metric thread. Interference landings
GOST 5359-77: Ocular thread for optical instruments. Profile and dimensions
GOST 6042-83: Round Edison thread. Profiles, dimensions and limit dimensions
GOST 6111-52: Conical inch thread with a profile angle of 60 degrees
GOST 6211-81: Conical pipe thread
GOST 6357-81: Cylindrical pipe thread
GOST 8762-75: Round thread with a diameter of 40 mm for gas masks and calibers for it. Main dimensions
GOST 9000-81: Metric thread for diameters less than 1 mm. Tolerances
GOST 9484-81: Trapezoidal thread. Profiles
GOST 9562-81: Trapezoidal single thread. Tolerances
GOST 9909-81: Thread taper valves and cylinders for gases
GOST 10177-82: Thrust thread. Profile and main dimensions
GOST 11708-82: Thread. Terms and Definitions
GOST 11709-81: Metric thread for plastic parts
GOST 13535-87: Reinforced thrust thread 45 degrees
GOST 13536-68: Round thread for sanitary fittings. Profile, basic dimensions, tolerances
GOST 16093-2004: Metric thread. Tolerances. Landings with clearance
GOST 16967-81: Metric thread for instrumentation. Diameters and steps
GOST 24737-81: Trapezoidal single thread. Main dimensions
GOST 24739-81: Multi-start trapezoidal thread
GOST 25096-82: Thrust thread. Tolerances
GOST 25229-82: Metric conical thread
GOST 28487-90: Tapered tool joint thread for drill string elements. Profile. Dimensions. Tolerances
Mechanical systems. GOST 9484-81: Basic norms of interchangeability. Trapezoidal thread. profiles. OKS: Mechanical systems and general purpose devices, Screw threads. GOSTs. Basic norms of interchangeability. Thread.... class=text>
GOST 9484-81
Basic norms of interchangeability. Trapezoidal thread. Profiles
GOST 9484-81
Group G13
INTERSTATE STANDARD
Basic norms of interchangeability
TRAPEZOIDAL THREAD
Basic norms of interchangeability. Trapezoidal screw thread. profiles
Introduction date 1982-01-01
INFORMATION DATA
1. DEVELOPED AND INTRODUCED by the Ministry of Machine Tool and Tool Industry
2. APPROVED AND INTRODUCED BY Decree of the USSR State Committee for Standards dated April 30, 1981 N 2264
3. REPLACE GOST 9484-73 in terms of profiles
4. The standard fully complies with ST SEV 146-78
5. RE-ISSUE
1. This standard applies to trapezoidal threads and specifies the profiles and dimensions of their elements.
2. The main thread profile, common to external and internal threads, and the dimensions of its elements must correspond to those indicated in Fig. 1 and in Table 1.
Outer diameter of the thread (screw); - outer diameter of the internal thread (nut); - average diameter of external thread; - the average diameter of the internal thread; - internal diameter of the external thread; - internal diameter of the internal thread; - thread pitch; - the height of the original triangle; - profile working height
Damn.1
Table 1
In millimeters |
||||
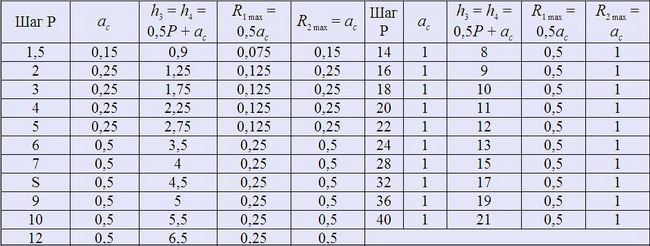
3. The nominal profiles of external and internal threads and the dimensions of their elements must correspond to those indicated in Fig. 2 and in Table 2.
Height of external thread profile; - height of the internal thread profile; - internal diameter of the external thread; - outer diameter of the inner thread; - rounding radius at the top of the external thread; - rounding radius along the cavity of the external and internal threads; - clearance at the top of the thread
Damn.2
table 2
In millimeters |
||||
4. Instead of rounding at the top of the external thread, it is allowed to make chamfers no larger than 0.5.
5. When threading, make the thread root profile rounded. In this case, reduce the internal diameter of the external thread by 0.15.
State standard USSR GOST 9484-81 (ST SEV 146-78)
"BASIC REGULATIONS OF INTERCHANGEABILITY. TRAPEZOIDAL THREAD. PROFILES"
Basic norms of interchangeability. Trapezoidal screw thread. profiles
Instead of GOST 9484-73 in terms of profiles
1. This standard applies to trapezoidal threads and establishes the profiles and dimensions of their elements.
The standard fully complies with ST SEV 146-78.
2. The main thread profile, common to external and internal threads, and the dimensions of its elements must correspond to those indicated in Fig. 1 and in table. 1.
Table 1
┌─────────────┬─────────────┬──────────────┬──────────────┬─────────────┐
│ Step Р │ Н = 1.866 Р │ Н │ Н_1 = 0.5 Р │ 0.366 Р │
│ │ │ ── \u003d 0.933 Р │ │ │
│ │ │ 2 │ │ │
│ 1,5 │ 2,799 │ 1,400 │ 0,75 │ 0,549 │
│ │ │ │ │ │
│ 2 │ 3,732 │ 1,866 │ 1 │ 0,732 │
│ │ │ │ │ │
│ 3 │ 5,598 │ 2,799 │ 1,5 │ 1,098 │
├─────────────┼─────────────┼──────────────┼──────────────┼─────────────┤
│ 4 │ 7,464 │ 3,732 │ 2 │ 1,464 │
│ │ │ │ │ │
│ 5 │ 9,330 │ 4,665 │ 2,5 │ 1,830 │
│ │ │ │ │ │
│ 6 │ 11,196 │ 5,598 │ 3 │ 2,196 │
├─────────────┼─────────────┼──────────────┼──────────────┼─────────────┤
│ 7 │ 13,062 │ 6,531 │ 3,5 │ 2,562 │
│ │ │ │ │ │
│ 8 │ 14,928 │ 7,464 │ 4 │ 2,928 │
│ │ │ │ │ │
│ 9 │ 16,794 │ 8,397 │ 4,5 │ 3,294 │
├─────────────┼─────────────┼──────────────┼──────────────┼─────────────┤
│ 10 │ 18,660 │ 9,330 │ 5 │ 3,660 │
│ │ │ │ │ │
│ 12 │ 22,392 │ 11,196 │ 6 │ 4,392 │
│ │ │ │ │ │
│ 14 │ 26,124 │ 13,062 │ 7 │ 5,124 │
├─────────────┼─────────────┼──────────────┼──────────────┼─────────────┤
│ 16 │ 29,856 │ 14,928 │ 8 │ 5,856 │
│ │ │ │ │ │
│ 18 │ 33,588 │ 16,794 │ 9 │ 6,588 │
│ │ │ │ │ │
│ 20 │ 37,320 │ 18,660 │ 10 │ 7,320 │
├─────────────┼─────────────┼──────────────┼──────────────┼─────────────┤
│ 22 │ 41,052 │ 20,526 │ 11 │ 8,052 │
│ │ │ │ │ │
│ 24 │ 44,784 │ 22,392 │ 12 │ 8,784 │
│ │ │ │ │ │
│ 28 │ 52,248 │ 26,124 │ 14 │ 10,248 │
├─────────────┼─────────────┼──────────────┼──────────────┼─────────────┤
│ 32 │ 59,712 │ 29,856 │ 16 │ 11,712 │
│ │ │ │ │ │
│ 36 │ 67,176 │ 33,588 │ 18 │ 13,176 │
│ │ │ │ │ │
│ 40 │ 74,640 │ 37,320 │ 20 │ 14,640 │
├─────────────┼─────────────┼──────────────┼──────────────┼─────────────┤
│ 44 │ 82,104 │ 41,052 │ 22 │ 16,104 │
│ │ │ │ │ │
│ 48 │ 89,568 │ 44,784 │ 24 │ 17,568 │
└─────────────┴─────────────┴──────────────┴──────────────┴─────────────┘
3. The nominal profiles of external and internal threads and the dimensions of their elements must correspond to those indicated in Fig. 2 and in table. 2.

table 2
|
h_3 = H_4 = 0.5 P + a_c |
R_1max = 0.5 a_c | |||
4. Instead of rounding at the top of the external thread, it is allowed to make chamfers no larger than 0.5 a_c.
5. When threading, make the thread root profile rounded. In this case, the inner diameter of the outer thread should be reduced by 0.15 R.


