Alisa Konyukhovskaya - [email protected]
The global industrial robotics market shows a high growth rate. Which regions and countries are world market leaders? Which industries show the greatest demand? At what level of development is the Russian market of industrial robotics? What are the limitations of development Russian market? The answers to all these questions are presented in this article.
Since 2010, the demand for industrial robots has increased significantly due to the trend of factory automation and technical improvements in industrial robots. Between 2010 and 2014 the average growth of their sales was 17% per year: between 2005 and 2008. about 115 thousand pieces were sold on average. robots, while between 2010 and 2014. the average sales volume increased to 171 thousand units. (Fig. 1). The increase in shipments was approximately 48%, which is a sign of a significant increase in demand for industrial robots around the world. In 2015, more than 250,000 robots were already sold, which was a new record for the market, which grew by 8% in a year. The greatest demand was registered in the automotive industry.
Regions
Asia(including Australia and New Zealand) is the largest market with about 139,300 industrial robots sold in 2014, up 41% from 2013. In 2015, over 144,000 industrial robots were sold in Asia.
Europe– the second largest market, where sales in 2014 increased by 5%, i.е. up to 45,000 pcs. In 2015, sales in Europe grew by 9% to reach 50,000 units. The most rapid growth in 2015 was demonstrated by the market of Eastern Europe – by 29%.
North America– the third market in terms of sales: in 2014, 32,600 units were sold, which is 8% more than in 2013, and in 2015, 34,000 units were sold, which was a new record for the region. In the first quarter of 2016, 7,125 robots were sold in the region for $448 million. Also, 7,406 robots were ordered by North American companies total cost about $402 million, which is 7% more than the volume of orders for the same period last year.
Leading countries
China – largest market industrial robots and the fastest growing market in the world. In 2014, 57,096 industrial robots were sold, which is 56% more than in 2013. Of these, about 16,000 robots were installed by Chinese suppliers, according to the China Robot Industry Alliance (CRIA). Sales were 78% higher than in 2013. This is partly due to an increase in the number of companies that provided their sales data for the first time in 2014. Foreign suppliers of industrial robots in China increased their sales by 49% , i.e. up to 41,100 units, including robots made by international manufacturers in China. Between 2010 and 2014 total shipments of industrial robots increased by an average of about 40% per year, and in 2015, China continued to show the highest growth, sales reached 66,000 units, and the market grew by 16%. This rapid development is a unique record in the history of robotics. A wide variety of industries in China are seeing increasing investment in factory automation.
AT Japan in 2014, 29,300 industrial robots were sold, the market grew by 17%. Since 2013, Japan has become the second largest market in terms of annual sales. Robot sales in Japan tended to decline from 2005, when sales peaked at 44,000 robots, until 2009, when sales fell to 12,800 units. Between 2010 and 2014 sales increased by an average of 8% per year.
Industrial robot market USA, the third largest in the world, increased by 11% in 2014, reaching a peak of 26,200 units. The driver of this growth is the trend towards production automation in order to strengthen the position? American industry in the world market and maintaining production in the home region, and in some cases with the aim of returning production from other regions.
Sales in Republic of Korea in 2014 increased by 16% to 24,700 units, slightly falling short of the 2011 record of 26,536 units. As in 2013, purchases of industrial robots from suppliers of automotive components (in particular, in the production of electrical components, such as batteries? etc.) increased significantly, while almost all other industries in 2014 bought significantly fewer robots. During 2010-2014 the annual sales of robots in the Republic of Korea has been more or less stable.
Germany is the fifth largest industrial robot market. In 2014, sales of robots increased by 10% to 20,100 units, which was a sales record. Deliveries of robots to Germany increased in 2010-2014. by an average of 9%, despite the high density of robots in the country. The main driver of sales growth in Germany was the automotive industry.
Since 2013 Taiwan ranks sixth among the most important industrial robot markets in the world in terms of annual deliveries to the country. The installation of robotic systems increased significantly between 2010-2014. - an average of 20% per year. In 2014, robot sales increased by 27% to 6,900 units. However, the number of installed robots in Taiwan is significantly lower than Germany, which ranks fifth with 20,100 units.
Italy is the second largest market for industrial robots in Europe after Germany and ranks 7th in the global ranking for the supply of industrial robots. Sales there increased by 32% to 6,200 units in 2014. Since 2001, this is the second such high level of annual sales, which is a clear sign of the recovery of the Italian economy. Between 2010 and 2013 annual sales in Italy were rather weak due to the crisis situation in the country.
Thailand is also a growing industrial robot market in Asia, ranking 8th in 2014 among other markets. 3,700 robots were installed - only 2% of the total global shipments.
AT India about 2,100 industrial robots were sold in 2014, a new peak for the country. Deliveries of robots to other South Asian countries (Indonesia, Malaysia, Vietnam, Singapore, etc.) increased in 2014: 10,140 units in 2014 compared to 661 units in 2013.
In France the market of industrial robots also recovered - 3,000 units (+36%). AT Spain sales of industrial robots decreased by 16% to 2,300 units. After a significant investment? between 2011 and 2013 sales in the automotive industry have declined markedly, although other industries have continued to increase investment in robotics. Sales of industrial robots in Great Britain dropped to 2,100 units in 2014 after significant investment? in the automotive industry in 2011-2012.
Demand for industrial robots by industry
The main "catalysts" for the growth of global sales of industrial robots are the automotive industry and electrical / electronics.
Since 2010, the automotive industry has been the most important customer of industrial robot manufacturers, significantly increasing investment in industrial robots around the world. In 2014, a new sales peak was recorded: about 98,000 new robots were installed in enterprises, which is 43% more than in 2013. The share of the automotive industry in the total number of deliveries of industrial robots is approximately 43%. Between 2010 and 2014 sales of robots in the automotive industry increased by an average of 27% per year. Investment in new production capacity in emerging markets and investments in modernization of production in the main countries producing cars, caused an increase in sales of robotics. In 2014, most of the robots were sold to manufacturers of automotive electronics components for the production of batteries and other electronic parts in cars.
Sales of robots for the production of electrical and electronics (including computers, equipment, radios, televisions, communication devices, etc.) increased significantly in 2014 and grew by 34% to 48,400 units. The share of the total supply is about 21%. Growing demand for electronics and new products, as well as the need to automate manufacturing, have been driving factors for accelerating demand.
Sales across all industries except automotive and electronics/electrics increased 21% in 2014. Between 2010 and 2014, the average idle rate was 17%. The sales growth rate for the automotive industry during this period was 27% and for the electrical/electronics industry 11%. This is a clear sign that the number of sales has increased not only in areas that are the main consumers of industrial robots (automotive and electrical and electronics), but also in other industries. Robot vendors report that the number of customers has shown significant growth in recent years. Although the number of robots ordered by the client is often very small.
Density of robotization
In many countries, there is a high potential for the use of industrial robots. Comparisons across countries of quantitative indicators, such as the total number of robotics units on the market, can be misleading. In order to take into account differences in the scale of the manufacturing industry, it is preferable to use an indicator of robot density. This density is expressed as the number of multifunctional robots per 10,000 workers employed in the manufacturing, automotive, or industry as a whole, which includes all industries except automotive.
The approximate global robot density is 66 industrial robots installed per 10,000 manufacturing workers (Figure 2). production with the most high level robotics are production facilities in the Republic of Korea, Japan and Germany. By continuing to expand the installation of robots over the past few years, in 2014, the Republic of Korea ranked first in terms of robot density (478 industrial robots per 10,000 workers). The density of robots in Japan continues to decrease: in 2014 it reached 314 units. In Germany, the reverse trend is observed: the density of robots has increased to 292 units. The United States of America is one of the top five global markets for robotic manufacturing, with a density in the US in 2014 of 164 machines per 10,000 workers. China is the most big market robotics in the world since 2013 - reached 36 pieces of equipment per 10,000 workers, which demonstrates a high potential for further installation of robots in this country.

In 2014, the density of robotization in the manufacturing industry by region was: 85 in Europe, 79 in America, 54 in Asia (Fig. 3).

The density of robotization in the automotive industry is higher. Despite an overall decline in robot density levels, this moment Japan has the highest density of robotics in the automotive industry (1,414 units installed per 10,000 workers). This is followed by Germany (1,149 vehicles per 10,000 workers), the United States of America (1,141 vehicles per 10,000 workers) and the Republic of Korea (1,129 vehicles per 10,000 workers).
Since 2007, the density of robotics in the automotive industry in China has increased significantly (305 units), but it is still at an average level. The reason for this is the large number of workers involved in this area. According to the China Statistical Yearbook, as of 2013, the automotive industry employed about 3.4 million people (including the production of auto parts). In 2014, about 20 million cars were produced in China, which was a record for the country and accounted for approximately 30% of all cars produced in the world. The necessary modernization and further increase in capacity will significantly increase the installation of robots in the coming years: the potential for installation of robotics in this market is still huge.
Russia
In Russia, sales of robots are extremely low - about 500-600 robots per year, the density of robotization is about 2 robots per 10,000 workers. In addition to the really low level of use of RTK in production, these figures are also due to the difficulty of obtaining data on the market, which is fragmented and, until recently, has not been purposefully studied. In 2015, the National Association of Robotics Market Participants (NAURR) was formed, which, in addition to the general tasks of market development, collects statistics and creates analytical materials on the robotics market.
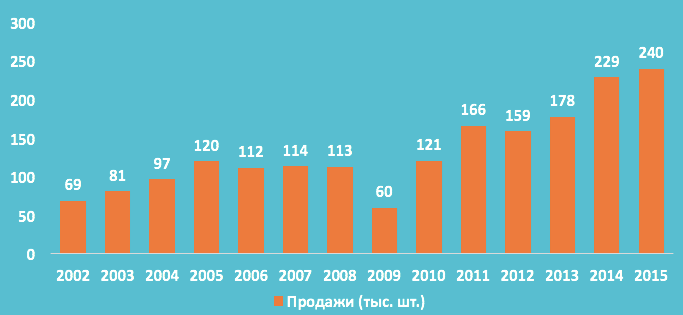
The total number of industrial robots installed by 2015 in Russian Federation– about 2,740 pcs. (Fig. 4). From 2010 to 2013, there was a steady growth in sales of industrial robots - an average of about 20% per year. In 2013, sales peaked at 615 robots (a 34% increase over 2012), but in 2014, sales dropped sharply by 56% to around 340 robots. The reason for this is a strong change in the exchange rate.

Preliminary sales figures for 2015 are about 550 robots. The leaders of the Russian industrial robotics market are KUKA and FANUC, which occupy about 90% of the market.
There are very few domestic manufacturers of industrial robots in Russia. In 2015, the Volzhsky Machine-Building Plant was closed, which for a long time was the only manufacturer of industrial robots in the country. In 2016, it is planned to launch a new plant for the production of industrial robots in Bashkiria. The Russian companies Record-Engineering, BIT-Robotics, Eidos-Robotics develop industrial robots, but their sales volume is still unknown.
In addition to manufacturers of industrial robots, important market players are system integrators who integrate the robot into the technological process. The cost of the robot itself can be about 50% of the price of a solution that requires specialized equipment, software settings, services, etc. There are about 50 integrator companies in Russia, which differ in their area of specialization and size.
One of the reasons for the low level of development of the industrial robotics market is the low awareness of enterprises about the possibilities of robotization of production processes and the associated cost reduction. Integrators almost do not calculate the real payback of RTK after installation, leaving it at the mercy of enterprises. It is possible to stimulate the development of industrial robotics in the country through the dissemination of systematized information on the real payback of RTK by industry and operations.
To study various barriers to the development of robotics (both industrial and service), the National Association of Robotics Market Participants in December 2015 conducted a survey of Russian robotics companies. Respondents' answers to the question about the restrictions that hinder the development of robotics in the Russian Federation, about the existing risks and barriers in the robotics market in general, are structured in the table into the groups "Education and Culture", "Technology", "Economy", "State", "Science" ".
| Group | The reasons |
| Education and culture |
|
| Technology |
|
| Economy |
|
| State |
|
| The science |
|
Overcoming the existing restrictions, of course, is impossible by the measures of one state; in order to form an industry development strategy, a broad dialogue of all market participants is necessary.
Thus, the global robotics market shows high growth rates (about 8%). The world leaders in the use of RTK in industry are China, Japan, South Korea, the USA and Germany. Russia, on the other hand, lags far behind in robotization of production for a number of reasons, which can only be overcome through communication and consolidation of participants in the robotics market.
The density of robotization in Russia is almost 70 times lower than the world average, the National Association of Robotics Market Participants (NAURR) found out. If in the world there were on average 69 industrial robots per 10,000 workers in 2015, then in Russia there is only one, according to the NAURR study (see graph). The leader of the ranking is South Korea, where there were 531 industrial robots per 10,000 industrial workers, Singapore (398) and Japan (305). An industrial robot is a programmed manipulator, explains NAURR President Vitaly Nedelsky.
The average annual sales of industrial robots in Russia are 500-600 units (550 were sold in 2015), which is about 0.25% of the world market, according to the NAURR study. By the beginning of 2016, a total of about 8,000 industrial robots were operating in Russia, while there are about 1.6 million of them in the world, follows from the document. The world leader in the number of industrial robots purchased in 2015 is China, whose enterprises purchased 69,000 devices, enterprises of South Korea purchased 38,300, Japan - 35,000. They are followed by the USA and Germany, which purchased 27,000 and 20,105, respectively, last year. robots.

Low demand in Russia is explained by the poor awareness of the technical management of enterprises about the capabilities of robots and the inertia of their thinking, Nedelsky is sure. After all, the purchase of a robot always results in the replacement of workers and updating the technological process. And the fact that most of the large industrial enterprises, which are usually the main consumers of robots, is in state hands, only increases inertia, continues Nedelsky.
There are few technologically advanced industrial enterprises in Russia, explains the low demand, the head of the Skolkovo robotic center, Albert Efimov. At the same time, robots appear at the enterprise almost last, when it has already solved all the problems with energy-saving production, organized labor, he continues. In addition, in Russia, a robot is much more expensive than labor, Efimov believes.
The robot solves a lot of personnel problems of the enterprise, Nedelsky is sure. He is able to work in three shifts, he can turn off the light and stop heating the room. Now the old workers are leaving, but the young ones are not coming in their place, and in the wake of the upcoming shortage of personnel in the industry, the management of enterprises is beginning to show interest in robots, says Nedelsky.
A few years ago, the Agency for Strategic Initiatives (ASI) announced that it would develop a robotization program for the economy, recalls Olga Uskova, President of Cognitive Technologies. However, neither the ASI, nor the Ministry of Industry and Trade or the Ministry of Economics got the program. ASI is not prepared for such work, she believes: since the agency is engaged in strategic issues, then he has a rather complicated and lengthy decision-making procedure, and the issue of robotization of the Russian economy has already left the category of strategic and moved to a tactical level, Uskova believes. According to her, this issue should be returned to the sphere of responsibility of the ministries.
According to the NAURR, in the world, robots are mostly employed in the automotive industry (38%), the production of electrical and electronics (25%) and mechanical engineering (12%). In Russia, 40% of robots are also used to create cars.
« Kamaz“Since the beginning of 2015, I have bought 26 robots and brought their total number at the enterprise to a hundred,” says plant representative Oleg Afanasiev. And by 2019, Kamaz will buy another 578 units, he promises. They are needed for the release of the new Kamaz lineup, says Afanasyev.
More than 600 robots are now working at the Gorky Automobile Plant of the GAZ group, engaged in stamping, welding, painting and casting, a representative of the enterprise said. 100 of them were purchased in the last two years. At the same time, the economic feasibility of using robots is not the only criterion, he points out, sometimes only a robot can act with the required accuracy and quality, a GAZ representative explains.
From 2005 to 2015, sales of industrial robots in Russia grew annually by 27%, but since 2016, the average sales growth should grow to 50%, NAURR believes. The association explains the acceleration of growth by attention from the state, the modernization of industrial processes large enterprises and raising awareness among technical executives of companies. Own production There are no industrial robots in Russia, the NAURR report says, but there are four Russian companies involved in the development of such production. According to Efimov, in 2017 such a development should appear in Skolkovo.
With service robots serving a person in medicine, education, etc., things are much better in Russia, Efimov says. He explains this by the fact that the Russian economy is much closer to the service model than to the industrial one. In addition, service robots are much more demanding on software than industrial robots that perform a limited set of actions. And in Russia they know how to write software, he notes.
The domestic robotics market can currently be called a free niche. The production of industrial robots in Russia is still very far from the level where supply will exceed demand. Many industrial companies enter into agreements with foreign companies, wanting to get a larger percentage of profits and increase market share through the modernization of production. The absence of state programs for the reorientation of domestic business to the domestic market significantly complicates and slows down the development of innovative production areas. But even in such a situation, worthy players of the Russian robotics market appear. Ucan is one of the leading manufacturers of commercial robotic units. The company's arsenal includes a number of modern solutions and a large staff of qualified software engineers. The combination of all factors indicates the high potential of the brand and its prospects.
How profitable is the production of robots in Russia
All currently existing robots used in industry can be classified according to such criteria as:- application area;
- location method;
- management principle;
- appearance;
- degree of autonomy.
- miniature (insect-sized) models with a radio module and sensors;
- large-scale complexes with several manipulators and a single control center;
- devices resembling familiar cars, planes or ships;
- freestanding compact complexes(terminals, photo booths, etc.);
- anthropomorphic mobile or stationary systems.
What functions can Russian-made robots perform?
 Depending on the type of device, robots can have different functionality, including performing the following types of work:
Depending on the type of device, robots can have different functionality, including performing the following types of work: - assembly and installation of industrial components and parts (welding, stamping, riveting, sorting, etc.);
- tracking and alerting;
- maintenance of generating and processing complexes;
- advising clients, providing background information and analytical activities;
- conduct of hostilities;
- providing two-way communication using audiovisual and tactile nodes.
 The sale of robots in Russia contributes to the modernization of production and business, offering functionality implemented through the installation of modern units for analyzing speech, visual and wave information in the equipment. A robotic complex or a separate machine receives information and processes it based on the embedded program code. Domestic robots are endowed with all the necessary components and work according to the classical principles used by the world's largest manufacturers. With the help of products offered by Ucan, you can create a fully automated complex that works without days off and breaks, does not require wages and even bringing a good profit. An excellent example is the model of the Couch series - which performs the functions of a coach, used during trainings, corporate training courses, seminars, etc. The production of industrial robots in Russia, as well as the organization of the rental of functional autonomous systems, can become profitable business with the right approach and organization. Ucan invites representatives of large businesses and individuals leading entrepreneurial activity. You can find out the details by visiting the official website of the company or by calling the phone that serves robot secretary capable of providing all the necessary information.
The sale of robots in Russia contributes to the modernization of production and business, offering functionality implemented through the installation of modern units for analyzing speech, visual and wave information in the equipment. A robotic complex or a separate machine receives information and processes it based on the embedded program code. Domestic robots are endowed with all the necessary components and work according to the classical principles used by the world's largest manufacturers. With the help of products offered by Ucan, you can create a fully automated complex that works without days off and breaks, does not require wages and even bringing a good profit. An excellent example is the model of the Couch series - which performs the functions of a coach, used during trainings, corporate training courses, seminars, etc. The production of industrial robots in Russia, as well as the organization of the rental of functional autonomous systems, can become profitable business with the right approach and organization. Ucan invites representatives of large businesses and individuals leading entrepreneurial activity. You can find out the details by visiting the official website of the company or by calling the phone that serves robot secretary capable of providing all the necessary information. the most promising companies and projects.
3.The largest and most famous robot manufacturers in the world:
6. Promising companies and projects in robotics for 2015 and further:
7.Robots / Robotics - Types of Robots, Best Robots:
List of existing and used robots in the world.
Humanoid robots.
Biorobots.
Industrial robots.
Underwater robots.
household robots.
Military, combat robots.
Trading robots in trading.
1.Global robotics market:
Market size from 15 to 30 billion dollars (the difference in estimates from what various experts consider robotics) taking into account the main segments - industrial and service robotics (military robots, domestic, for educational purposes, to help the disabled and toy robots (world market volume service robotics is estimated at 5.3 billion dollars)).
Sales of industrial robots from 2013 to 2014 increased from 160 thousand pieces. up to 178 thousand pieces, sales of service robots from 2013 to 2016 according to experts, they should reach the level of 15.5 million units. household robots, 3.5 mln. robotic toys, 3 mln. for educational purposes, and 6.4 thousand pieces. to help the disabled.
Major Buyers industrial robots - Japan, South Korea, China, USA, Germany, countries major robot manufacturers - Japan and Germany(more than 50% and about 22%, respectively, of the global production of industrial robots).
Biggest Demand and production growth expected in production - personal, educational, household robot assistants, industrial(assembly, welding, painting, etc.), rehabilitation, various kinds mobile, medical, surgical, agricultural, construction and military robots.
Boston Consulting Group predicts an increase in investment in industrial robotics until 2025 (further in more detail) among the 25 largest economies in the world - up to 10% per year, compared with 2 - 3% at present. The investment will pay off in cost savings and efficiency gains. Robots are getting cheaper. The cost of a spot welding robot, for example, has dropped from $182,000 in 2005 to $182,000. to $133,000 last year and will drop to $103,000 by 2025. Accelerated automation will make it possible to revise the criteria for choosing places for opening and expanding production facilities, as a result of which, the availability of cheap work force may become a less significant factor, this will allow the return of part of the production back to the US and the EU from countries with lower wages.
October 2014 Oxford University published a study on the prospects for the use of robotics, which suggests that over the next two decades, up to 47% of today's jobs in the US could be replaced by robots.
President of China Robotics Association (CRIA) Song Xiaogang reported that the number of robots sold in China in 2014 will reach 50,000, up from 36,860. in 2013. “…The robotics industry will maintain an annual growth rate of 40% for an extended period of time,” he said. "China has already overtaken Japan as the world's largest consumer of robots, buying more than one-fifth of all robots produced globally."
2. Russian market of robotics:
The share of Russia in the modern robotics market is only about 0.17%. According to the company Neurobotics volume domestic market ready-made robots and components in the next year or two should be about 30 thousand pieces, or about 3 billion rubles.
The average cost of an anthropomorphic robot (with human resemblance) is now $450,000. According to the chief roboticist Skolkovo Foundation Albert Efimova, now about 300 robots are sold in Russia a year: This is 500 times less than in developed countries. In addition to major foreign automotive brands, almost no one is involved in the introduction of robotic technologies in our country.
In Russia, there are about 2 robots per 10 thousand employees of enterprises in the manufacturing industry, in China and South Africa - about 24, in Brazil 5, in India, about the same as in Russia.
The peculiarities of the robotics market include long, labor-intensive and capital-intensive stages of research and development, as well as the creation of prototypes of developed products, so participation and assistance from the state is of great importance in this area.
The Russian robotics market is represented mainly by space and special robots- sappers, scouts. These devices are manufactured under defense order, and the details of government contracts were not disclosed. In addition, centers at institutes are often engaged in robots, which do not involve commercial activities. Therefore, it is difficult to judge the production volumes of robotics enterprises in the Russian Federation.
Therefore, how the figure of 0.17% was obtained in 2013 (Russia's share in the market of industrial robots) is a big question.
Nevertheless, with all the possible conditionality of estimates of robotics in Russia, the gap between the highly developed countries in the world and the Russian Federation in the field of robotics certainly exists.
Successful models of robots applicable for industry remain single copies produced for scientific and applied purposes and do not go into mass production. Household robots are of very little interest to Russian roboticists. For 2014, according to International Federation of Robotics, the total number of robots working in our country amounted to approximately 4 thousand.
However, even while the only industry developed in Russia robotics - military has great development prospects. Despite a noticeable lag in this area, the combat and special robots of Russian scientists are still gaining recognition at international arms exhibitions and receive special awards.
1:04 Modern robots: drones, scouts, sappers.
3. The largest and most famous
robot manufacturers in the world:
Leading positions in the development, production and promotion of industrial robotics are occupied by the largest international corporations, holdings and companies, such as:
iRobot Corporation(USA). Specializes in military robots- sappers, rescuers, scouts, as well as household- vacuum cleaners and washing robots. By 2013 the company has sold more than 10 million home robots. For 10 years from 2004 to 2014. the company increased sales from $95 million to $505 million and profit from near zero to $25 million a year. The most famous and popular robots of the company:
household robots:
- AVA with on-board computer;
- Verro, created for cleaning pools;
- Roomba and Create, performing the functions of a vacuum cleaner;

military and security robots:
- SUGV combat system, which performs the functions of evacuation and data transmission in military conditions;
- Warrior, created to neutralize explosive mechanisms, move the wounded and extinguish fires;
- submersible Seaglider;
- Ranger carrying out water patrols;
- mini device LANdroids to support communication that receives the signal from Apple devices.
ABB(Sweden - Switzerland). One of the leaders in the robotics market, the company was formed as a result of the merger of ASEA and Brown, Boveri & Cie. Specializes in industrial robots different levels of difficulty. The company is building a plant in Russia, the first stage will be commissioned in mid-2015.
FANUC Robotics(Japan). Produces mostly industrial robots: for welding and palletizing, painting, portal, delta robots. Created the strongest robot with a load capacity of 1350 kg. capable of lifting loads up to 6 m.

KUKA(Germany). In 1973, she created the world's first industrial robot. The robots of this company are widely used in the automotive industry. The robot also makes Robocoaster which is used as an amusement ride . Produced more than 100 thousand robots.

Kawasaki Robotics(Japan). Produces industrial robots- for work in aggressive environments, in explosive environments, robots for universities, spider robots. More than 120 thousand robots of their production are installed worldwide.
Mitsubishi(Japan). Engaged in the creation industrial robots used:
- in the production of mobile devices;
- when performing loading and unloading operations;
- in the automotive industry;
- in the installation of small parts on laboratory and medical equipment.
LG Electronics(South Korea). Part of the LG Group, one of the largest manufacturers of home appliances, produces robots for home such as robotic vacuum cleaners.
Kaman Corporation(USA) Specializes in production of combat, military and industrial robots.
Sony (Japan). Perhaps the most famous development of the company is bipedal robot QRIO. This intelligent android has a capacious operating memory, is able to pick up and move things, move around, go down stairs and dance, and produce other playfulerobots, for example, robot dogs. The first copy appeared in 1999.

Honda(Japan). Created asimo humanoid robot who can talk, recognize faces and walk.

Panasonic(Japan). One of the largest manufacturers of household appliances, produces industrial robots, such as robot hairdresser washing people's heads learning industrial robots, robot runners and robot vacuum cleaners.
LEGO Group(Denmark) Produces robotic kits- constructors to create programmable robot.
Yujin Robot(South Korea). The company is known for creating affordable robot toys and household devices. One of the company's most sought-after projects is Iclebo robot vacuum cleaner capable of performing wet cleaning.
Intuitive Surgical(USA). The main product of the company is da Vinci Surgical System, the prototype of which was designed more than 30 years ago. This device, equipped with 4 arms, is capable of performing surgical operations.

Consis. Engaged in the development pharmacy robots- manipulators who assist pharmacists. These devices are installed in drug storage areas, where they optimize drug storage and retrieval processes. The system allows to reduce the time of customer service, increase the turnover and rationally use the place of storage of medicines.
Gostai(France). Creates robots of the Jazz series. The devices operate in telepresence mode and are equipped with basic computer applications. A robot connected to Wi-Fi is controlled using a browser. Jazz provides navigation and night patrols.
AIST. Produces humanoid robot HRP-4C, with the appearance of a young girl. The developers were able to accurately copy the features and faces of the human body. The device is able to sing, recognize speech and surrounding sounds.

Aldebaran Robotics(France). Created humanoid robot NAO, which is distinguished by its ability to use gestures, identify voices, and respond to commands. The robot can interpret current events, make decisions according to the current situation and learn.

Takara Tommy. i-SODOG Interactive Puppy Takara Tomy has the ability to memorize and learn. Artificial intelligence the robot dog allows it to respond correctly to 50 voice commands. The robot can dance to music, recognize voices and smells.
Cubic Robotics. The company has created home assistant Cubic capable of turning electrical appliances on and off, recognizing human speech, talking with the owner.
Engineering Arts. Robot actor Robo Thespian created by the company is endowed with a system of facial and skeletal muscles. The device is able to play scenes from films, create their own scenarios.

Innovation First(USA). Micro robots series Hexbug created in the form of insects. it robot toys, which can crawl, find a way out of complex mazes and serve as bait for pets.
Other large and well-known companies in the robotics market:
Yaskawa Electric, Comau, Reiss, Stäubli, Kaman Corporation , Nachi-Fujikoshi, Thyssen,Adept Technology, American Robot, Omron, RoboGroup TEK, Rockwell Automation, ST Robotics, Yamaha Robotics,Kawasaki, Durr,toshiba,General Motors (GM) …and many others.
ATIn total, there are about 400 companies involved in the production of robotics in the world market.
4. Manufacturers of robots and robots in Russia:
State Scientific Center of the Russian Federation Federal State Autonomous Scientific Institution "Central Research and Development Institute of Robotics and Technical Cybernetics"- created in 1968 in St. Petersburg. Main directions - mechatronics, mobile robotic systems, cybernetics of space, sea, air and ground-based, robots and manipulators for work in extreme conditions.
CJSC "Center for High Technologies in Mechanical Engineering at MSTU. N.E. Bauman" Moscow - products: sapper robots, scouts, land combat robots, walking robots. Net profit for 2012 increased from 1.95 million rubles. up to 5.35 million rubles
JSC "NIKIMT-Atomstroy" - the head materials science organization of Rosatom, located in Moscow, produces mobile robots and their control systems. The net loss of JSC "NIKIMT - Atomstroy" for 2012 decreased by 2.4 times to 311.83 million rubles. from 749.30 million rubles. for the same period last year.
Research Institute for System Research RAS Moscow - releases transport robots, robotic equipment for the production of computers, software.
NPO "Android Technology" is a relatively young company, founded in 2005, headquartered in Moscow. Engaged in production android robots, avatar fighting robots, this year the robot avatar will be tested. Uses robotic system SAR-400 to participate in space research. The robot can perform service and emergency work in conditions hazardous to human life. The annual turnover and revenue of the company are not advertised.
FSUE TsNIIMash Korolev, founder "Roskosmos". The institute team created a space anthropomorphic robot SAR-400. Planned in 2015 project "Exchange", as a result of which technologies for information exchange and control of robots on the surface of the Moon and other planets will be created. According to the results of 2013, the revenue of OAO NPO TsNIIMASH increased to 1.7 billion rubles.

OJSC TSNIITOCHMASH Rostec State Corporation, Moscow Region, Klimovsk. Founded in 1944. One of the promising developments in cooperation with the Advanced Research Foundation - anthropomorphic combat robot under the control of the operator. The robot, using a manipulator arm, shoots a pistol at a target and rides a quad bike. The enterprise produces the most massive types of weapons and military equipment for various branches of the military, including robotic observation and sighting devices for air and ground weapon carriers and military equipment.
1:25 Avatar robot.
SPKB PA located in Kovrov, developed the design mobile all-terrain vehicle "Varan" for mass production ultralight robots- scouts and sappers. "SKB PA" for 2012 received a profit from sales of 82.19 million rubles.
MIREA (Moscow State Technical University of Radio Engineering, Electronics and Automation) - developed a remote manipulation mini-robot control system through the Internet, intelligent onboard control system for air, ground and underwater robots, intelligent vacuum cleaner.
"Scientific Research Technological Institute (NITI) Progress" in Izhevsk, he owns the development of the latest robotic complex "Platform-M" for the Russian army. This armored robot with a remote control, a grenade launcher and a machine gun, fights without contact with the enemy, is used for reconnaissance and security. Capable of destroying stationary and moving targets. The first production samples have already been delivered to the Russian Armed Forces.
1:44 Tests of a combat robot with a machine gun and a grenade launcher.
Izhevsk Radio Plant — specializes in robotic systems, for example, mobile robotic complex MRK-002-BG-57, destroys stationary and mobile targets, provides fire support and reconnaissance, robotic complex-sapper, MRK-VT-1- a complex on a caterpillar track, controlled by radio at a distance of up to 1 km.
Institute for Problems in Mechanics named after A.Yu. Ishlinsky Academy of Sciences Moscow - deals with mobile robots: several types - walking, on wheels or on suction cups- for moving on surfaces of arbitrary inclination, robots moving inside pipes, miniature mobile industrial robots.
Research Institute of SteelMoscow - created a unique multifunctional robotic mini-loader MKSM 800A-SDU with remote control, rescuer and sapper for work in aggressive environments. Conducts nuclear, biological and chemical reconnaissance.
SMP Robotics company - Zelenograd, created and put into production patrol robots - "Tral Patrol 3.1". Protects large areas and detects moving objects on it.
Other presence robots and generalist robots (Russian development):
Robot wagon - can be a telepresence robot, a promoter and even a bartender, developed by the company CJSC "RBOT" telepresence robot R.Bot. Price from 379,000 rubles.

Mobile Autonomous System - remote presence robot Webot from company Wicron allows you to perform actions at the location of the robot using a computer and the Internet. The robot allows you to remotely monitor what is happening and talk to people, see the world around you and calmly move through it at the speed of a walking person. Price from 300,000 rubles.

CCTV and telepresence robot - developer NIL AP(Scientific - research laboratory of design automation). Skype on wheels or a webcam with a microphone and loudspeaker - rides and turns in the right direction. Management can be carried out from anywhere in the world via the Internet from any computer or smartphone, without installing special software - just enter the site BotEyes.ru under your username and password. Price from 1 390 am. Doll.
telepresence robot -Synergy Swan from company "RBOT", using technology for robots with interchangeable intelligence, which provides an optimal price / quality ratio compared to functional analogues on the market. Price from 59 900 rubles.

telepresence robot - remote control and teleconferencing from the company padbot, allows you to navigate and conduct video conferences in online mode via computer or phone. PadBot app is available for both iPhone, iPad, Android phones and tablets, web-based management will become available in the near future. Price from 35,000 rubles.
Dean-Soft.Robot waiter, the software of which was created in the company Dean-Soft, maybe - follow the guests, distribute menus, deliver dishes, take payments, collect dishes.

5.Robotics - global perspectives:
Boston Research Company (BSG) as part of a global study of the robotics market predicts up to 2025. its average annual growth rate in 10,4% . Including and first of all:
- Order 15,8% annual growth in the segment of personal robots - robots for training and education, entertainment, security, cleaning and other household purposes. Sales will grow to $9 billion by 2025. from 1 billion dollars in 2010
- Order 11,8% annual growth in sales of robots for medical, surgical purposes, in agriculture and construction. Sales will grow to $17 billion by 2025. from 3.2 billion dollars in 2010
- Order 10,1% annual growth in sales of robots in production - for welding, assembly, painting, loading and unloading and other types of work. Sales will grow to $24.4 billion by 2025. from 5.8 billion dollars in 2010 Thus, this segment of robotics, despite the lower growth rates, will retain a large share of the robotics market.
- Order 8,1% annual growth in sales of robots for military purposes - primarily unmanned aerial vehicles, military exoskeletons, underwater vehicles and ground Vehicle. Sales will grow to $16.5 billion by 2025.
All this will take place against the backdrop of falling prices of robots and components with an increase in their productivity and complexity of the work they perform, which in turn will lead to an expansion of the range of their use.
6. Promising companies and projects
in robotics in 2015 and further:
The EU is funding 17 new robotics projects. Projects under common name Horizon 2020, each of which focuses on the development of significant robotic technologies for industrial and service use. The emphasis is on rapid technology transfer followed by commercialization, so each project has at least one corporate partner.
1.AEROARMS - robotic systems with multiple manipulators and advanced capabilities for the aerospace industry.
2.AEROWORKS - flying robots for autonomous inspection and maintenance of urban infrastructure.
3.COMANOID - robotic solutions for complex or tedious human operations aircraft assembly Airbus.
4.CENTAURO - human-robot symbiosis, in which the operator controls the robot arms.
5.CogIMon - humanoid robot to interact with humans and robots.
6.FLOBOT - floor cleaning robot in industrial, household and office premises.
7.Flourish- promising agricultural robots.
8. RETRAINER - robot assistant in the process of rehabilitation for people who have had a stroke, and to restore the functions of the arm and hand.
9.RobDREAM- improved industrial mobile robotic arms.
10.RoMaNS - robotic system to clean up accumulated nuclear waste.
11.SARAFun - two-armed robot for assembly operations based on ABB YuMi.
12.EurEyeCase - surgical robots for eye operations.
13.SecondHands - robot assistant, which provides assistance during routine preventive maintenance operations.
14.Smokebot - development of mobile robots with new environmental sensors for surveying disaster sites with low visibility.
15.SoMa - development of soft elements of robots for safe interaction with humans and the environment.
16.Sweeper- provision of automated harvesting of sweet peppers.
17.WiMUST- expansion and improvement functionality existing marine robotic systems.
…other recent significant events, trends in the world:
Drones- Chinese company DJI one of the world's largest manufacturers of consumer unmanned aerial vehicles (drones) is trying to raise up to $10 billion to expand production.

Robotic Manipulators - company ABB announced the acquisition of a German robotics company Gomtec in order to expand its product range with so-called collective or collaborative robots. Lightweight, flexible robotic arms from Gomtec are a family of six axial modular robots of the "collective" type called Roberta, with base price from € 27 900 before € 32 700 .
Robotic vacuum cleaners - are becoming more and more popular in the world, moving from the category of curiosities to the category of consumer goods. Company iRobot in 2014 has already sold 12 million brand vacuum cleaners Roombas from the beginning of their sales. Robotic vacuum cleaners now account for 18% of the global vacuum cleaner market and their share is growing at an annual rate of 21.8% (company iRobot occupies 83% in the North American, 62% in the European and Middle East and 67% in the Asia-Pacific markets). Another Chinese company Ecovacs, in just one day managed to sell 73,300 pieces. vacuum cleaners, most of which were robot vacuum cleaners Ecovacs Deebot.
7.Robots / robotics - types of robots,
best robots:
List of existing and used robots in the world: pharmacy, biorobot, industrial, transport, underwater, household, combat, zoorobot, flying robot, medical robot, microrobot, nanorobot, personal robot, pediculator, robot artist, pharmacy robot, toy robots, robot waiter, robots - programs, robot - a surgeon, a robot - a guide, a social robot, a ball robot, a humanoid robot, a trading robot in trading.
Humanoid robots:
Robot playing ping pong - Topio on the international exhibition robots, distant 2009. Tokyo.

Company SCHAFT Japan, owned Google- Rbot "S-One", weighs 95 kg, equipped with two "legs" and two "arms". The height of the apparatus is 1.48 m, the width is 1.31 m.
1:54 SCHAFT DARHA Robotics Challenge 8 Tasks + Special Walking
"Aiko" - robot girl, speaks Japanese and English, can solve mathematical problems, understands more than 13,000 sentences, sings songs, reads newspapers, is able to identify various kinds of objects, etc.

Biorobots:
Frank- Designed and developed by the Smithsonian Institution in the USA. The world's first biorobot, consisting of 28 body parts, copying human ones - the heart, lungs, kidneys, etc. function. The robot talks and moves, but does not have independent thinking, there is no facial expressions.
1:21 A biorobot with a face and organs will be shown to the public.
Industrial robots:
Industrial robotics mainly designed for use in manufacturing and assembly robots in the automotive, electronics, and food and beverage industries. Most often, robots are used to automate processes such as welding, painting, assembly, product control, testing and package. There are several types of industrial robots: SCARA, articulated robots, Cartesian robots, cylindrical robots. These robots are used in heavy engineering to perform functions such as welding and soldering, supply of raw materials and material processing, grinding and coloring, etc.
According to company analysts TechNavio, the average annual growth of the world market of industrial robotics in mechanical engineering will be 6.27% in the period from 2013 to 2018.
Nissan's robotic assembly shop, 2010. new plant - Kanda city, Japan.

2:29 Panasonic industrial robot.
Underwater robots:
Household robots:
Military, combat robots:
In the world:
10:33 US military robots.
Russia:
3:05 "Russian Terminator" Russian combat robots
have no analogues in the world!*(Really?
Trading robots in trading:
2:55 Algorithmic system. Trading robot.
Trading robot created by the team "United Traders" won first place in the competition "The Best Private Investor-2011". For 2.5 months, its profitability amounted to almost 8 000 % per annum! Developers trading robot for trading from United Traders do not exclude that the trading robot developed by them for trading in the American markets, quite possibly, today has no competitors in Russia, and possibly throughout the world. Trading is always a plus, since several strategies are used at once, and if one of them starts to give drawdowns, it is immediately excluded and the next one is switched on.
The best opportunities for using a trading robot in trading are the so-called high frequency trading or scalping, where earnings largely depend on the number of successful transactions, each of which individually brings not a lot of income, in total allows you to earn significant funds per day. However, the use of trading robots in such transactions allows you to make thousands of such transactions per day (increasing the final profitability by an order of magnitude), since a person is physically incapable of such transactions.
Currently no less 95% from the total number of applications to 40% from actual trading volumes on MICEX exhibited and carried out trading robots. In the derivatives market (forwards, futures, options, swaps), the share of trading robots in the total number submitted bids and trade volumes is at least 90% and 60% respectively.
Industrial robots, automation and robotization of production, Industry 4.0 - we hear and read all these phrases in various variations almost every day. But who in the world today is engaged in the development and production of such machines that are needed in industry? We have compiled an overview of these companies for you.
Of course, there are many more companies - we have identified only the most significant of them, as well as those that are developing industrial robots in Russia and the CIS countries. If you think that we unfairly forgot about someone - write in the comments.
FANUC was founded in 1956 by Dr. technical sciences Seihuemon Inaba, who introduced the concept of numerical control (CNC) from the first day of her work. Starting in the late 1950s with the automation of individual pieces of equipment, a few decades later, FANUC was already involved in the automation of entire production lines. And the basis for such innovative growth was the invention of Dr. Inaba: he created the first electric stepper motor, applied numerical program control and installed this engine in the machine.
Constantly pushing the boundaries of automation, improving product quality and productivity, and reducing costs, Dr. Inaba and his team have designed machine loading robots.
When first-class products such as ROBOCUT, ROBODRILL and ROBOSHOT were introduced into production in the 1970s and 80s, FANUC provided optimized solutions for a variety of applications to meet the requirements of different customers. In Japan, FANUC has become the first company to build and operate an automatic plant with CNC machines and robots.
FANUC, founded 60 years ago, is the world's leading manufacturer of factory automation equipment, with over 3.6 million CNC controllers and 400,000 robots installed worldwide.
The range of FANUC industrial robots is very wide. The company offers a whole series of robots with different characteristics, capable of performing a wide variety of tasks. production tasks: delta robots, robots for painting, welding, palletizing, for mounting from above, articulated robots, among which the record holder today in terms of load capacity is 2300 kg! As well as recently introduced collaborative robots that can work side by side with a person.
A Japanese corporation headquartered in the cities of Kobe and Tokyo (Minato), established by Kawasaki Shozo in 1896; one of the world's largest industrial concerns. Initially, the company was engaged in shipbuilding, but at the moment the main products produced are industrial robots, jet skis, tractors, trains, engines, weapons, light aircraft and helicopters, as well as parts for Boeing, Embraer and Bombardier Aerospace aircraft. Kawasaki's products also include motorcycles and ATVs (a division of Consumer Products and Machinery). But we are interested in industrial robots, which the company has been dealing with since 1969.
Kawasaki robots can be used in the most different areas: assembly from small parts weighing only a few grams, moving massive workpieces weighing up to 1.5 tons, various welding methods, painting, palletizing. In addition, Kawasaki's line of robots includes medical and cleanroom robots, as well as a collaborative two-armed robot.

The Yaskawa Electric Group was founded in 1915 and consists of 78 subsidiaries and 21 partnerships with Yaskawa Electric as the parent company. The group has approximately 8,000 employees worldwide and is headquartered in Kitakyushu, Japan. In addition to robotics, YASKAWA is also active in systems development, motion control and information technologies and is one of the world's leading manufacturers of servo motors, amplifiers, inverters and controllers for the automation and drive industries, offering both standard products and customized solutions. YASKAWA independently produces all the main components and technologies for its robots and uses the latest technology in a one-of-a-kind factory in Japan where robots produce robots.
Each year, Yaskawa Electric Corporation produces 1.6 million inverters, 800,000 servo drives and 22,000 MOTOMAN industrial robots, which find their way into a wide variety of industries around the world. To date, more than 270,000 units of MOTOMAN robotics have been installed in the world, including robots for painting, welding, palletizing, loading, working in clean rooms, etc.

NACHI robots are manufactured in Japan by parent company NACHI-Fujikoshi Corp. The main products of NACHI Corporation are electronic equipment, robotic systems, precision machinery, cutting tools, bearings, hydraulic equipment, automotive parts, special steels and coatings. Currently, the NACHI group includes 47 companies, 26 of them are located in Japan, 21 - outside of it. The company's turnover last year exceeded 1 billion 100 million US dollars.
Nachi Fujikoshi is a leading manufacturer of industrial robots that are used by many well-known manufacturers around the world. The line of robots is divided into two: standard, which includes robots of light, medium and heavy classes, as well as for working with a press, and special robots for working in clean rooms.

OTC-DAIHEN Corporation in Osaka (Japan), founded in 1918, occupies a leading position in the world in the production of high-tech welding equipment and robotics. It is not for nothing that 80% of factories in Japan, trusting in the experience and professionalism of OTC-DAIHEN in the field of welding production, have given their preference to cooperation with this company, which is a leader in its field. Among them are such giants of the Japanese industry as Toyota, Mitsubishi, Honda, Mazda, Nissan and others.
Daihen's first generation of OTC arc welding robots was developed in the late 1970s. Since that time, the company has been actively improving and developing the direction of robotic welding and developing a specialized line of robots. OTC Daihen welding robots are used for arc and resistance welding and plasma cutting.

DENSO Corporation was founded in 1949. When the first industrial robots appeared in the 1960s, DENSO began to develop and apply new technologies in its own production processes, which allowed her to constantly improve and upgrade hardware and software. The company's first industrial aluminum robot was developed in 1970.
Today, DENSO Robotics is the world leader in small industrial robots and continues to set the tone for reliability, flexibility and functionality. The company has installed more than 60,000 robots worldwide, of which it uses 16,000 in its own production facilities.
Seiko Epson Corporation better known as Epson - structural subdivision Japanese diversified concern Seiko Group. One of the largest manufacturers of inkjet, dot matrix and laser printers, scanners, desktop computers, projectors, and robots for mounting small parts.
Epson robots first appeared on the world market back in 1984. Originally created to meet the needs of internal automation, Epson's robots have quickly become popular in many well-known manufacturing sites around the world. Over the past 30 years, Epson Robots has become a leader in the small parts assembly robotics industry and has brought many innovations, including PC-based control, compact scara robots, and more. To date, more than 55,000 Epson robots have been installed in factories around the world. Many of the leading manufacturing companies rely on these robots every day to reduce production costs, improve product quality, and increase productivity.

Comau is an Italian multinational company based in Turin and part of the FCA Group. Comau is an integrated industrial automation company with an international network of 35 operating centers, 15 manufacturing enterprises and 5 innovation centers around the world. The company offers complete end-to-end solutions, services, products and technologies with competencies ranging from metal cutting to fully robotic manufacturing systems to meet specific manufacturing needs in industries ranging from automotive, rail and heavy industries to renewable energy and other industries.
Comau releases various models industrial robots with a load capacity of up to 800 kg.
The applicability of Comau robots is standard for any robots with anthropomorphic kinematics: welding technologies, palletizing, machining, application of compositions: painting, primer, adhesives, sealants.

Panasonic is not only a world-famous Japanese engineering corporation with almost a century of history (the company was founded in 1928), which produces household appliances and electronic goods, but also one of the market leaders in industrial robotics and welding equipment.
Panasonic Robots is a division of the global Panasonic Corporation, which specializes in the development, production and sale of industrial robots for various purposes. In particular, Panasonic's welding robot is an all-in-one technology, with no additional interface between the robot and the welding source. Today, sales of Panasonic welding robots have reached 40,000 units. The company also produces universal manipulators for many types of production tasks.
Panasonic robots are highly reliable, long service life and relatively low cost. Currently, they are successfully used in the automotive, petrochemical, mechanical engineering, and logistics (cargo handling) industries.

Adept Technology Inc. is a multinational corporation headquartered in California. The company specializes in industrial automation and robotics, including software. Adept was founded in 1983. It all started when company founders Bruce Shimano and Brian Carlyle, both graduate students at Stanford University, started working with Viktor Sheinman at the Stanford Artificial Intelligence Lab.
Today the company is active in various industries requiring high speed, processing accuracy, including processing food products, consumer goods and electronics, packaging, automotive, medical and laboratory automation, as well as emerging markets such as solar panels.

Universal Robots is a Danish manufacturer of small flexible production collaborative robots, the so-called. collaborative. The company was founded in 2005 by three Danish engineers. In the course of joint research, they came to the conclusion that at that time the robotics market was dominated by heavy, expensive and bulky robots. As a consequence, they developed the idea of making robotics accessible to small and medium enterprises. In 2008 the first UR5 cobots were introduced to the Danish and German market. In 2012, the second robot, UR10, was launched. At automatica 2014 in Munich, the company launched a completely revised version of its collaborative robot. A year later, in the spring of 2015, the new UR3 robot was introduced.

BIT Robotics creates new equipment for new technological processes. BIT Robotics is the creator of the first Russian industrial delta robot. The robot created by delta is not inferior to the most modern and high-speed foreign analogues in terms of characteristics. The most advanced materials, including composite ones, are used in its design.
The company's capabilities and competencies allow creating any robotic systems, widely using servo systems and technical vision. The company's engineers have rich experience. Most of them are from the space and aviation industries. The company has the most modern production equipped with CNC machines, a foundry, a galvanizing shop, a production of polymer materials, etc.



