One of the main factors that have a significant impact on the efficiency of corporations is organizational and managerial measures, including the system of accounting, cost control and output. These problems currently remain the weakest point in corporate financial management. As a result, many corporations incur expenses not only for the main production, but also for penalties, taxes and payments, as well as compensation for losses from the theft of inventory and finished products.
In this regard, there is an objective need to organize such a corporate management accounting system that would allow controlling costs at any time within any technological process with differentiation by place of origin. Such a system will be the basis for making operational management decisions. It should be noted that the correctness of accounting and management accounting of costs in corporations depends not only on the fulfillment of regulatory requirements, but also on taking into account the features inherent in a particular industry.
In our opinion, in order to systematize the control of labor costs and the consumption of inventory items for production, a strict reflection of production costs for all technological processes is of great importance. That is, these processes in corporate management accounting become the main cost points.
In addition to technological features, the effectiveness of the cost accounting system is influenced by forms of management, of which the most important, in our opinion, are:
organization of labor and its payment;
break-even business process;
corporate marketing;
interaction of various business processes.
These organizational features necessitate the implementation of corporate cost accounting for departments (business processes). It seems to us that this is due not only to the need to obtain timely information when operational management production processes, but also with the possibility of increasing the personal interest of workers in a particular process in increasing the quantity and quality of products.
For operational control and management of great importance is the accurate timely preparation and presentation of primary documents, reporting materially responsible persons in corporate accounting. For an objective assessment of the contribution of each business process to the consolidated efficiency by type of activity of the corporation, management accounting should ensure timely and complete posting of products, the correct assessment of their quantity and quality, separate accounting of output by business processes, objectivity and reliability of data from primary documents and registers accounting.
In Russian conditions, when using the concepts of consolidated accounting and reporting, one can proceed from the fact that we are talking about the integration of performance indicators of economic entities contained in the following reporting forms:
income statement;
cash flow statement.
The need for consolidated reporting appears when structures are created in real economic life, for example, corporations connected by mutual participation in each other's capital or otherwise. Objects for consolidated reporting arise for a variety of reasons. A corporation acquires other business entities to expand its business, generate income from investments, eliminate competitors, or establish close formal relationships for mutual benefit.
The presence of a corporation's consolidated reporting makes it possible to increase its financial and socio-economic manageability, to have an objective picture of activities in general and each business process in particular, and to invest resources in truly promising areas.
The essence of the consolidated financial statements of a corporation is that:
a) it is not the reporting of a legally independent economic entity and has a clearly expressed analytical focus. The purpose of such reporting is not to identify taxable income, but to obtain general idea on the activities of business processes within the corporation;
b) the process of consolidation is not a simple summation of articles of the same name financial reporting corporate business processes. In the process of consolidation, any intra-corporate financial and business transactions are excluded, and only assets and liabilities, income and expenses from transactions with third parties are shown in the consolidated financial statements.
Studies show that information of a financial and economic nature about the performance of a corporation as a whole is necessary for:
external management bodies - in order to determine the role and place of the corporation in the economic development of the state and the region in particular; identifying the degree of coincidence of interests of federal, local governments and corporations in the implementation of economic development programs declared by the corporation at the time of its registration, i.e. whether this corporation is a development tool industrial production in the conditions of structural restructuring of the state economy or the direction of its activities is subject to change or correction;
internal consumption by the corporation - in order to develop a common effective corporate strategy for development and activities, increase the manageability of its participants, the implementation by the participants of the corporation of a single, coordinated financial, economic and social policy;
informing the general public, existing and potential investors about the activities of this corporation, allowing them to judge the amounts, time and risks associated with expected income, as well as the economic resources of the corporation, its obligations, the composition of funds and sources, the reasons for their changes.
Thus, the consolidated financial statements contain information characterizing the totality of business processes operating within the framework of a single economic strategy and participating (to one degree or another) in each other's capital. It is necessary for everyone who has or intends to have interests in this corporation: investors, creditors, suppliers, customers, personnel, banks, government authorities.
The creation of a financial strategy in the corporate management of an insurance company is a paramount task of financial management, especially it is of great importance in modern conditions development of the market, characterized by an ever-increasing increase in supervision and control over the activities of the company and in particular its financial results.
The purpose of corporate governance in a broad sense is the process of finding a compromise between the interests of various participants in a corporation, namely: between shareholders and managers, individual groups of individuals and corporations as a whole. The corporate governance system in an insurance company increases the company's profit by finding an approach to each client, facilitates paperwork, translating most of the documents into electronic form. It also allows you to more competently conduct insurance activities.
Insurance companies are an investment institution in the financial market. Their activity is based on a license. Not only trust in the company on the part of controlling and supervisory state bodies depends on a well-formed financial strategy, but also trust on the part of existing and potential customers in the future. Insurance activity is represented by a high degree of risks and excessive uncertainty. It provides protection against economic and natural risks, contributes to increasing the stability and reliability of the country's socio-economic well-being.
The economic and financial foundations of the activities of an insurance organization differ from other various types commercial activities. First of all, the differences relate to the formation of financial potential and maintaining the financial stability of the insurer. Achieving the financial stability of the insurance company is provided by the following indicators: the amount of the paid authorized capital of the insurance company; the size of insurance reserves; system of reinsurance of insurance rates; profitable portfolio of placement of insurance reserves and other indicators.
The sources of finance for an insurance company include the insurance premium and income from the investment activities of the organization. The company's own funds are formed from two channels of income: from the contributions of the founders and from the profits received. It should be noted that own funds are exempt from any external obligations. To achieve the financial stability of the insurer, certain requirements are established for the size of the authorized capital. The minimum amount of the redeemed authorized capital is 120 million rubles, the amount of the minimum authorized capital for life insurance companies is 240 million rubles; professional reinsurers have an amount of 480 million rubles. In all cases, the maximum liability for a single risk cannot exceed 10% of the insurance company's own funds. The main criterion in assessing the financial stability of an insurance organization is the compliance with the size equity the amount of commitments. Insurers must comply with the normative ratio between the accepted insurance liabilities and assets. Assets - represent the property of the insurer in the form of materials, fixed assets, financial investments and cash. Liabilities represent the insurer's debt to legal and individuals. They include bank loans and credits, insurance reserves and other attracted and borrowed funds, settlement obligations for reinsurance operations and other accounts payable, reserves for future payments and expenses.
A financial strategy is a general plan of action, the purpose of which is to provide a corporation with cash. It covers the issues of practice and theory of financial redistribution, their provision, and also ensures the financial stability of the organization in market conditions management. The financial strategy of the organization, includes: optimization of fixed assets, profit distribution, capital management, tax management, cashless payments, market policy valuable papers. Without accounting in the financial strategy, the company may become bankrupt.
Companies can develop several types of financial strategies: a general, operational financial strategy and a strategy for the implementation of individual strategic tasks. The most holistic is the general financial strategy. It includes several operational financial strategies, but at the same time it does not act as a simple sum of them. The general financial strategy develops the company's activities for a long and predictable period of time.
The operational financial strategy of the organization specifies the general strategy planned for a short period of time and implements part of the tasks set by the general financial strategy. As a rule, it is developed for a month, a quarter. This strategy is aimed at mobilizing internal reserves and controlling the use of funds.
The strategy for achieving private goals deals with the provision and implementation of the main strategic goal. It does not contradict the objectives of the general and operational strategy. After determining and approving the overall financial strategy of the corporation, special units in accordance with the state financial market and, in accordance with the chosen strategy, predict the credit and investment strategy corporations. This approach allows you to “direct” the activities of departments in accordance with the goals of the corporation, and helps top management organizations to plan the development of other areas of activity, as shown in Figure 1.
Rice. 1. The structure of the financial strategy of the corporation.
The complexity of forming the financial strategy of an insurance company lies in the difficulty of identifying the financial results of the organization. The financial result of insurance companies in many countries is determined in the traditional way by comparing income and expenses for a certain period. This approach is based on the standards from the state when calculating the financial result for taxation. State bodies establish regulations, which regulate information about the requirements for calculating the taxable base. The report on the results of the insurance organization is presented in the reporting form and is attached to the balance sheet of the insurer, which is published annually. The information is open to all interested parties, which is associated with the socially significant nature of insurance protection.
The financial strategy in its content in the corporate management of an insurance company includes a financial target strategy and a financial resource strategy.
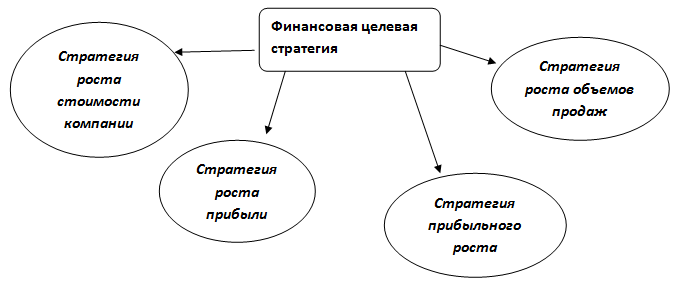
Rice. 2.Financial target strategy of the insurance company.
When forming a targeted financial strategy, one must always remember and take into account the interests of various interested groups: shareholders, customers, top managers, and personnel. Next, consider the resource financial strategy.

Rice. 3. Financial resource strategy of the company
The financial resource strategy depends on the company's financial goals and funding sources. The self-financing strategy involves investing a certain part of the profits received by the company to expand the business. The strong advantages of such a strategy include building a company with unified business processes and common standards and with a common organizational culture. The above strategy involves the development of certain areas of the strategic plan. The investment financial strategy is formed using borrowed funds in the market or shareholders. This strategy assumes the existence of an investment project that serves the goals of the target financial indicators of the plan of the insurance organization.
The investment strategy differs from the self-financing strategy in that financial resources for development are allocated on a paid basis. The most widely used classical discounting cash flow. This involves the implementation of such stages as the implementation of the project and the assessment of its feasibility, as well as the development of an investment project. Profit in insurance is usually considered in two aspects: profit as financial results and profit in tariffs or normative profit. The normative profit when calculating the tariff is already included in the price of the insurance service. It is the estimated profit of the insurer, planned for a certain type of insurance. However, insurance operations may not always provide the expected result. The total amount of profit by type of insurance is determined by comparing gross income with expenses. When analyzing the financial and economic activities of insurance companies, a special category includes profit from the investment activities of a corporation. The services provided determine the insurer's extensive investment opportunities.
Indicators financial activities insurance company are background information for general management. Its purpose is to identify the "bottlenecks" of the business and identify areas that increase its profitability and efficiency. The financial strategy of an insurance company is not static; it largely depends on the situation in the financial market and is subject to the influence of competition.

Rice. 4. Stages of formation and implementation of a financial strategy that ensures the competitiveness of an insurance company.
There are four types of financial strategies defined by two factors: the first factor affects the ability of an insurance organization to increase sales growth and finance the differentiation of insurance products; the second factor increases the allowable cost limit in the insurance organization.
The first and second strategies are typical for rapidly developing insurance organizations that are focused on selling differentiated insurance products. There is a generation of surplus of financial resources and Insurance companies may increase allowable costs.
The other two strategies are being used by underfunded insurers to finance rapid sales growth. This is achieved by increasing the variety of types of insurance products.
As a result, the choice of a financial strategy is a complex process, which must take into account the criteria for the growth of sales of differentiated insurance products, the level of costs acceptable to the company. Financial strategies rely primarily on a system of financial indicators. The effectiveness of the formation of implementation and financial strategies as a whole depends on the literacy of their development, comprehensive accounting and assessment of internal and external factors that affect the successful operation of insurance organizations.
Bibliographic list
- Blank, I. A. Financial strategy of the corporation Text. / I. A. Blank. -K.: Nika-Tsentr, 2004. 720 p.
- Ulybina L.K. Methodological aspects of the equity capital adequacy strategy of an insurance organization in the context of market transformation and globalization / L.K. Ulybina // Financial Analytics: Problems and Solutions. 2012. No. 17 - S. 26-29.
- Fundamentals of insurance activity: Textbook / Ed. Ed. Prof. T.A. Fedorov. - M .: Publishing house BEK, 2005 - p. 634.
- Ulybina L.K. Investment potential of insurance companies / L.K. Ulybina, V.N. Verbenko, O.A. Okorokova // Economic and socio-environmental transformations in the system of sustainable development North Caucasus region: materials of interregional. scientific-practical. conf. Belorechensk, 2009. 0.4 p. (author - 0.2 p.l.).
- Law of the Russian Federation of November 27, 1992 N 4015-1 (as amended on November 28, 2015, as amended on December 30, 2015) “On the organization of insurance business in Russian Federation” (as amended and supplemented, effective from 09.02.2016). [Electronic resource] // Access mode https://www.consultant.ru/document/cons_doc_LAW_1307/
- Financial strategy [Electronic resource] // Access mode http://www.consensus-audit.ru/
- OA Management of insurance reserves of insurance organizations / OA Okorokova // Financial analytics: problems and solutions. - 2012. - No. 02. - P. 48-51.
- Zadykhaylo, D. V. Corporate management: textbook. allowance / D.V. Zadykhaylo, O.R. Kibenko, G.V. Nazarov. - H. : Espada, 2003. - 688s.
- Okorokova O. A. Financial strategy of an insurance company / O. A. Okorokova // Bulletin of Adygeisky state university. Series 5: Economy. - 2011. - No. 3. - S. 29-36.
- Khalyapin A. A. The current state of insurance in Russia / A. A. Khalyapin, Kh. I. Karimova // In the collection: Patterns and trends in the formation of the system of financial and credit relations. Collection of articles of the International scientific-practical conference. Managing editor: Sukiasyan Asatur Albertovich. Ufa, 2016. - S. 281-283.
- Blyumgardt A. Models of corporate governance. - K .: Nauk thought, 2003. - S. 13-14
- Zhavoronkova, Yu. V. The main stages in the development of a financial strategy Electronic resource. / Yu. V. Zhavoronkova // Access mode http://www.rusnauka.com
- Ulybina L.K. Management of own capital adequacy and risks of insurers / L.K. Ulybina, O.A. Okorokova // Polythematic network electronic journal Kuban State Agrarian University ( Science Magazine KubGAU). [Electronic resource]. Krasnodar: KubGAU, 2013. No. 85 (01). Access mode: http:/ej.kubagro.ru/2013/01/pdf/09.pdf. 0.4 p.l. (author - 0.2 p.l.).
480 rub. | 150 UAH | $7.5 ", MOUSEOFF, FGCOLOR, "#FFFFCC",BGCOLOR, "#393939");" onMouseOut="return nd();"> Thesis - 480 rubles, shipping 10 minutes 24 hours a day, seven days a week and holidays
Skachkova Natalya Evgenievna Formation of the financial strategy of the corporation: Dis. ... cand. economy Sciences: 08.00.10: Krasnodar, 2005 165 p. RSL OD, 61:05-8/3124
Introduction
Chapter 1. Theoretical and methodological foundations for the formation of the financial strategy of a corporation 14
1.1. Corporation as a participant in financial relations 14
1.2. The essence of the financial strategy of the corporation and the factors that determine it 28
1.3. The concept of the financial strategy of the corporation.. 42
Chapter 2. The mechanism for implementing the financial strategy of the corporation 59
2.1. Formation of financial resources of the corporation 59
2.2. Optimization of the capital structure of a corporation 74
Chapter 3. The effectiveness of the financial strategy of the corporation 101
3.1 Market value as a criterion for the effectiveness of a corporation's financial strategy 101
3.2. Conditions for the effectiveness of the financial strategy of a corporation 114
3.3. Corporation Market Value Management Algorithm 131
Conclusion 146
List of sources used 154
Introduction to work
Relevance of the research topic. Structural adjustment Russian economy Against the backdrop of the ongoing process of privatization of state and municipal enterprises became the objective reason for the emergence and development of corporations. The gradual integration of Russian corporations into the world economy in the context of the increasing complexity of the market environment, the internationalization of the financial system, the globalization of capital markets actualizes the issues of formation strategic management the activities of corporations. The key direction of strategic management is its financial component, which is designed to provide economic efficiency and the stability of the process of reproduction of corporate capital, due to the intensity and dynamism of the financial relations of the world economic system.
The need for scientific understanding of the formation of an effective financial strategy is determined by the process of development of Russian corporations in the framework of the transformation market relations and the growing importance of financial strategy as an element contributing to the involvement of domestic companies in the process of cross-country capital flows. With the integration of Russian corporate capital into the global financial system the formation of a corporation's financial strategy is becoming an important applied area of economic science.
During the period of initial market transformations of the domestic economy, due attention was not paid to the strategic aspect of the activities of corporations, the problems of organizing effective financial and economic activities covered the operational and tactical levels, and profit maximization was considered as the financial goal of the functioning of corporations. However, the ongoing processes of development of the stock market, the intensification of mergers and acquisitions, the growing professionalism of shareholders and investors orient the owners of corporate
capital to a qualitatively new level of choice of the purpose of functioning - the maximization of the value of the corporation. Along with the spread of the cost approach in the practice of corporate financial management, its theoretical and methodological foundations remain insufficiently developed and systematized.
Various theoretical aspects the formation and development of corporate structures, the formation of strategic management of companies have been studied by many foreign and domestic scientists. There are several qualitatively different levels of scientific development of this problem.
The fundamental foundations for the formation and management of corporate entities were laid in the works of I. Ansoff, D. Bell, A. Burley, M. Weber, W. Gates, R. Hilferding, R. Jackson, E.J. Dolan, P. Drucker, J. M. Keynes, T. Keller, W. King, D. Cleland, T. Kono, V. Lenin, K. Marx, A. Marshall, G. Minza, J. Mossin, J. Pierce, K. Popper, M. Porter, J. Robinson, A. Toffler, F. Hayek, M. Hammer.
The problems of financial management of companies are considered in the works of R. Ackoff, V. Bard, F. Black, R. Braley, Y. Brigham, A. Denisov, D. Duran, I. Egerev, L. Igonina, D. Kidwell, S. Myers, G. Markowitz, M. Miller, F. Modigliani, V. Narsky, I. Nikonova, M. Scholes, V. Slepov, J. Tobin, O. Williamson, R. Holt, J. Van Horn, W. Sharpe.
The process of privatization in Russia led to the emergence of new scientific developments of domestic scientists devoted to the problems of the formation of corporate structures in the Russian economy (I. Balabanov, I. Belyaeva,
A. Bushev, A. Volodin, V. Goncharov, A. Zhuplev, T. Kashanina, O. Rodionova, O. Syroedova, V. Shein). The financial aspects of the strategic management of domestic companies are reflected in the works of A. Bandurin, V. Bocharov, G. Gref, V. Gurzhiev, V. Efremov, V. Ivanchenko, G. Kleiner,
B. Kovaleva, M. Kruk, A. Movsesyan, R. Nurgaliyeva, A. Radygina, I. Khominich. At the same time, insufficient attention has been paid to a systematic study of the processes of formation of the financial strategy of corporations as special subjects of financial relations; this problem remains undeveloped in many aspects.
The conditions for the market transformation of the Russian economy determine the study theoretical foundations formation of the financial strategy of the corporation using modern scientific approaches that involve a more active inclusion of the concept of market value in the strategic financial management of the corporation. The creation of an effective mechanism for the formation of a financial strategy that is adequate to the targets of corporations in a dynamic market environment contributes to their sustainable development, which reflects the demand for such developments in domestic corporate practice.
The designated scientific and practical problem, which is fundamental in its significance for the development of the entire domestic corporate sector and its interaction with other sectors of the economy, should be solved on the basis of the totality of theoretical knowledge and accumulated practical experience, including international. This circumstance determined the choice of the purpose and objectives of the dissertation research.
The purpose and objectives of dissertation research. Target
dissertation research is to develop the theoretical foundations for the formation of the financial strategy of the corporation, providing
achieving the maximum market value, and substantiating an effective mechanism for implementing the corporation's financial strategy in the context of ongoing market transformations and the integration of the Russian economy into the world economy. The implementation of the goal required the solution of logically related and consistently implemented tasks:
Clarification of the concept of "corporation" as a participant in financial relations;
The study of the essence of the financial strategy of a corporation and the identification of the main factors that determine the financial strategy of a corporation in modern Russian conditions;
Substantiation of the concept of the financial strategy of the corporation;
Development of a mechanism for the implementation of the financial strategy, based on the clarification of the functions of the corporation's finances;
Determination of a set of actions to optimize the financial structure of the corporation's capital, providing effective implementation the process of formation and use of financial resources;
Establishing a criterion for the effectiveness of a financial strategy that determines an objective assessment of the financial and economic activities of a corporation;
Development of an algorithm for managing the market value of a corporation, aimed at implementing an effective financial strategy. The object of research are corporations as participants
financial relations that form the financial strategy in the conditions of market transformations of the Russian economy.
The subject of the dissertation research is the financial relations that arise in the process of forming the financial strategy of Russian corporations, in the context of market transformations, the transformation of the domestic economy and the adaptation of corporate governance practices to the requirements of developed corporate capital markets of the modern world economic system.
Theoretical and methodological basis of the dissertation research
the fundamental concepts presented in the works of foreign and domestic scientists who implement the Keynesian, neoclassical, institutional approaches to the analysis of the problems of the formation and development of corporate financial relations in a transitional economy served. In the course of the study, the provisions of the theories were used transaction costs, investment value, portfolio investment, capital structure, company value management.
Instrumental and methodological apparatus of work. In the process of studying the financial strategy of the corporation, general scientific
methods of cognition (dialectical, system-functional, complex, institutional), as well as private methodological means economic developments(financial, investment, economic and mathematical, statistical analysis, economic and statistical groupings, expert assessments, forecasting, modeling of economic phenomena).
Russian and foreign monographic literature, publications in periodicals, regulations of ministries and departments of the Russian Federation, statistical materials served as the information and empirical basis for the dissertation research. Federal Service state statistics, materials of corporate structures, informational resources"Internet". In the course of the study, general and special literature, legislative and other regulations, developments of domestic and foreign scientists in the field of functioning of corporate structures were studied. The applicant's own analytical developments published in scientific journals were also used.
The working hypothesis of the dissertation research is to put forward and substantiate a system of provisions, according to which the formation of an effective financial strategy of a corporation in the conditions of market transformations and the strengthening of the integration of the Russian economy into the world economy implies an orientation towards achieving the maximum market value of the corporation; market value management is carried out by influencing the financial factors that form it.
1 The main provisions of the dissertation research submitted for defense:
1. The transformation of the Russian market system served as the basis for the emergence and development of corporations. Corporation as a subject of financial relations acts as a form of organization entrepreneurial activity, based on the pooling of capital, expressed in securities that are in free float on the stock market; the priority goal of the corporation is to maximize the market value; within the organizational structure of the corporation, the division of ownership and management functions is positioned.
2. The financial strategy is the definition of priority goals and a system of actions to achieve them in the field of formation of financial resources, optimization of their structure and effective use, corresponding to the general concept of the development of the corporation and ensuring its implementation. The financial strategy of a corporation is determined by the action of a complex of interrelated factors: macroeconomic factors (level of development and financial market conditions, mechanisms state regulation activities of corporate structures); meso-economic factors (sectoral and regional); microeconomic factors (the possibility of attracting financial resources in the market, the level of qualification of financial management and its ability to organize an effective financial policy, etc.). Forecasting trends of change and regulation of these factors create the basis for the development of an effective financial strategy that is adequate to the state of the internal and external corporate environment.
3. Analysis modern approaches to the choice of the purpose of the functioning of the company (the theory of agency relations, the theory of transaction costs, the theory of portfolio, the theory of capital structure, the theory of company value management) and the combination of their resources in relation to the corporation make it possible to single out the maximization of market value as a priority goal of the financial strategy. The achievement of this goal is based on the implementation of the financial strategy of the corporation through the implementation of the functions of the corporation's finances (formation of financial resources; optimization of the financial structure of capital; use of financial resources).
4. The study of scientific approaches to the analysis of the dependence of the cost of capital on its structure allows us to determine a set of actions aimed at optimizing the capital structure of a corporation, which includes: a retrospective analysis of the correlation of structure indicators
capital with the amount of cash flow generated by the corporation; factor analysis capital structure (financial market conditions, sectoral features of the functioning of the corporation, stage life cycle, the level of profitability of operating activities, the structure of assets, the stability of sales, the level of tax burden); setting the allowable value of the cost of capital.
5. The key directions of the mechanism for implementing the financial strategy of corporations are determined by the functions of the corporation's finances: the formation of financial resources, optimization of their structure and effective use. An analysis of the financial strategies of corporations in the Russian telecommunications industry indicates the formation of a trend of dominance of borrowed sources in the composition of financial resources, an aggressive increase in investment, an increase in the asymmetry of profitability and destabilization of the financial condition. The result of the implementation of this strategy is the low capitalization of corporations, which does not correspond to the level of "faire value" (fair value).
6. The stock market that has developed in Russia, due to the specifics, which consists in the incompleteness of the process of forming the legal framework, the absence of a mass market for the shares of open joint-stock companies and the speculative nature of the securities market, does not reflect the actual market value of corporations. In this regard, it is advisable to determine the reasonable market value on the basis of methodological tools for assessing the market value of a company that exists in the professional practice of global valuation activities.
7. The study of approaches to the formation of an effective corporate governance mechanism at the present stage of development of the Russian market economy allows us to identify a number of basic conditions for the effectiveness of the financial strategy of a corporation: legal support, consisting in the development and adoption of the necessary framework laws and by-laws, as well as their effective enforcement; an effective mechanism for intracorporate
management; information openness aimed at increasing professional level interaction of the company with shareholders, investors and other participants in financial relations.
8. A study of the development of the paradigm for determining the value of a corporation made it possible to single out as the resulting indicator of the effectiveness of a financial strategy - economic value added - Economic Value Added (EVA), correlation financial factors which (return on invested capital - ROI, weighted average cost of capital of the company - WACC), is a set consisting of two fields: the field of creating economically added value and the field of loss of economically added value.
9. The value creation process expresses the functional dependence of two variables: the correlation of weighted average costs and return on invested capital; stages of a corporation's life cycle. A different combination of the indicated variables allowed the applicant to form the final matrix of financial strategies for managing the value of the corporation. Depending on how the key financial factors are correlated at each stage of the life cycle, the strategies were classified into three groups: financial strategies for creating the value of the corporation; financial strategies to retain the value of the corporation; corporate depreciation financial strategies.
The scientific novelty of the dissertation research lies in the substantiation of the theoretical foundations for the formation of an effective financial strategy focused on maximizing the market value of a corporation, and the practical development of an effective mechanism for managing the market value of a corporation by influencing the key financial factors that form it, taking into account the peculiarities of this process in Russian conditions. The elements of scientific novelty are as follows:
The concept of "corporation" as a participant in financial relations has been clarified (a form of business organization based on
the pooling of capital, expressed in securities that are in free circulation on the stock market, characterized by the separation of ownership and management functions), the direction of the functioning of this economic entity is revealed, consisting in the transition from profit maximization in accordance with the neoclassical understanding of the purpose of the company's activity to the maximization of market value , an adequate theory of company value management;
Based on the clarification of the functions of the finance of the corporation, the essence of the financial strategy of the corporation is revealed, which is the definition of priority goals and a system of actions to achieve them in the field of the formation of financial resources, optimization of their structure and effective use, corresponding to the general concept of the development of the corporation and ensuring its implementation;
The concept of the corporation's financial strategy as a system of interrelated and subordinate elements (goal, objectives, principles, mechanism for implementation, performance evaluation) is substantiated, focused on maximizing the market value of the corporation;
A model for the formation optimal structure of the corporation's capital, which includes: analysis of the dynamics of the correlation of indicators of the capital structure with the value of the cash flow generated by the corporation; analysis of factors affecting the structure of capital; determination of the allowable value of the cost of capital;
An algorithm for managing the market value of a corporation has been established, which includes: assessment of the market value of a corporation, selection of key financial factors, analysis of the influence of key financial factors on the value of a corporation, optimization of key financial factors; the implementation of the market value management algorithm helps to ensure the effectiveness of the financial strategy, which consists in maximizing the market value of the corporation.
The theoretical significance of the study is determined by the development of the theoretical foundations for the formation of a financial strategy aimed at maximizing the market value of a corporation in the context of market transformations in the Russian economy. Theoretical conclusions and results of the study of the role of a corporation as a participant in financial relations at the micro-, meso- and macroeconomic levels, the construction of the process of formation and the mechanism for implementing a financial strategy and its structuring can be used to further clarify and systematize scientific views in the field of corporate financial relations.
The practical significance of the dissertation research lies in the fact that the proposed practical advice can be used by Russian corporations to form a financial strategy and build an effective mechanism for the strategic management of the value of a corporation in the context of the development of the Russian market economy.
Separate results of the dissertation research can be used to improve the structure, content and teaching methods of such disciplines of higher education as: "Financial Management of Enterprises", "Strategic Management", " Financial management”, “Financial strategy of companies”.
Approbation of work. The main provisions, theoretical and practical conclusions formulated in the dissertation research were reported at international, all-Russian and regional scientific-practical conferences, scientific-practical seminars: International seminar "Alternatives for economic growth in Russia" (Sochi, 2003); The first regional scientific and practical conference "Economy of the North Caucasus region on the way to sustainable development in market conditions" (Krasnodar, 2003); XI, XII scientific and practical conferences "Science of the Kuban" (Krasnodar, 2003-2004); XIII All-Russian Scientific Conference on Economics "Globalization and Problems of Russia's Economic Development"
(Krasnodar, 2003); Interuniversity scientific and practical conference of young scientists (Krasnodar, 2004).
The results of the study are reflected in 9 printed works with a total volume of 2.7 pp, the author's contribution - 2.4 pp.
Work structure. The structure of the dissertation reflects the logic and specificity of the author's approach to the study of the problem. The dissertation consists of an introduction, three chapters, including nine paragraphs, a conclusion, a list of references, which contains 174 titles. The work is presented on 165 pages of the main text, contains 28 tables, 14 figures.
Corporation as a participant in financial relations
The corporation is a form of financial and industrial association, typical for countries with developed market economies. At the same time, in the context of the globalization of the world economic space, corporate structures freely function in economic systems of various levels of development.
Corporations dominate other business entities and are the most active participants in financial relations. According to experts, in the modern world there are about 40 thousand corporate structures, which include approximately 180 thousand branches in 150 countries. They concentrate up to 50% of industrial production and trade in developed countries, about 80% of all patents and licenses for the latest technology, technology and know-how. According to the United Nations, in 2003, the 100 largest US corporations, each of which includes enterprises in 25 industries, accounted for up to 60% of US GNP, 45% of employees, 60% of gross investment. While the world economic system is based on large and super-large organizational structures, modern Russian corporations are going through a period of formation.
Obviously, the scientific approach requires a clear definition of the concepts used. Let's consider the main approaches to the definition of "corporation" and highlight its essential properties. The most complete definition of a corporation can be found in the Big Commercial Dictionary1: “Corporation is a form of business organization that is widespread in countries with developed market economies, providing for shared ownership, legal status and concentration of management functions in the hands of the upper echelon of professional managers (managers), hired workers." It must be emphasized that within the framework of global economic integration, the level of economic development is not a factor limiting the functioning of international corporations that operate in less developed economies.
It should be noted that a number of Russian economists, in most cases, put an equal sign between a corporation and a joint-stock company, using the concept of "corporation" to denote the fact of separating the ownership of capital from the management function. So, R.G. Yemtsov understands a corporation as a form of business organization in which ownership and management are clearly separated from each other. Category " joint-stock company» the author introduces as the second designation of the corporation1. V.P. Georgians, in turn, are distinguished by the concepts of "joint-stock company" and "corporation". Under the joint-stock company, the scientist understands the organizational form in which authorized capital is divided into a certain number of shares, and a corporation is a joint-stock company that combines the activities of several firms to achieve their common goals or protect privileges. Thus, the concept of "corporation" is used to mark the complex nature of an organization that operates on the basis of joint ownership, common goal-setting and protection of privileges.
Formation of financial resources of the corporation
AT economic literature there is no single approach to the definition of the concept of "financial resources". Most authors consider financial resources from the point of view of the enterprise, without paying attention to organizational form companies. However, the corporation, due to its essential characteristics, has specific opportunities for the formation of financial resources, which must be identified.
Let's consider the main approaches to the definition of the concept of "financial resources" of an enterprise and evaluate them from the position of a corporation. So, L.N. Pavlova defines financial resources as their own sources of financing for expanded reproduction, remaining at the disposal of the enterprise after the implementation current liabilities on payments and settlements1. It should be noted that only a few enterprises operating in a stable economy can rely on their own sources of financing, while most of them are also forced to use borrowed and borrowed sources.
According to P.A. Petrova: "Financial resources are a set of own, attracted and borrowed funds necessary for the normal functioning of the financial mechanism of an enterprise." Despite the complete list of resources - "the totality of own, borrowed and borrowed funds", the author limits their capabilities exclusively to "normal functioning". There is no doubt that financial resources must also be considered as a source of expanded reproduction, which goes beyond the scope of “normal financing”, for all enterprises, regardless of their organizational form.
According to E.G. Guseva, the company's financial resources are a set of funds in the form of income and external receipts intended to fulfill financial obligations and incur costs to ensure expanded reproduction. This definition is also not without a drawback, which is the exclusion of capital from the sources of financial resources, while it is the basis for their formation.
According to the applicant, the most complete definition was proposed by M.V. Romanovsky, “the financial resources of an enterprise are all sources of funds accumulated by an enterprise to form the assets it needs in order to carry out all types of activities, both at the expense of its own income, savings and capital, and at the expense of different kind receipts". Dignity this definition consists both in the fact that the whole range of sources of financial resources is covered, and in the fact that the directions of their use are indicated.
Based on the study of approaches to determining the financial resources of an enterprise, we will formulate a definition of the financial resources of a corporation. It seems that the financial resources of a corporation can be defined as all sources of funds (own, borrowed and attracted) intended for the subsequent servicing of the financial relations of the corporation. As a specific characteristic of the financial resources of a corporation, we denote the following, corporate entities have a unique tool for attracting financial resources - this is the issue and placement of securities through the stock market.
Market value as a criterion for the effectiveness of a corporation's financial strategy
Russian and foreign scientists pay great attention to the study of issues related to determining the effectiveness of the financial activities of enterprises. So, in the works of a number of domestic economists (L.T. Gilyarovskaya, E.V. Negasheva, R.S. Saifulin, A.N. Selezneva, A.D. Sheremet), the concept of "efficiency" is used in connection with the study of financial and economic activities of the enterprise based on management reporting data, which allows assessing the impact of such production indicators, as capital productivity, resource productivity, material productivity, etc.
O.V. Efimov and M.N. Kreinina identified a different approach, in which efficiency is considered as a tool for financial analysis, where the leading role is played by profitability and turnover indicators.
According to V.V. Kovaleva, the assessment of the effectiveness of the current activities of the business activity of an enterprise is a combination of three components: assessment of the degree of implementation of the plan according to the main indicators and analysis of deviations; assessment and provision of acceptable rates of increasing the volume of financial and economic activities; assessment of the level of efficiency in the use of financial resources commercial organization, analysis of profit and profitability. The concept of "efficiency" is defined by the author as "a relative indicator that measures the effect obtained with the costs or resources used to achieve the effect"1. As an effect, an absolute performance indicator is considered, for the enterprise this indicator is profit.
The concept of "efficiency" is also studied among foreign scientists. So, K. Walsh considers efficiency through indicators of magnitude total assets, return on net assets and return on invested capital1.
R. Kaplan in his work “System balanced scorecard» critically assesses the approach of determining the effectiveness of the organization's activities only financial indicators, and proposes to study the functioning of the company according to four criteria: financial, customer relations, internal business processes and training, staff development. At the same time, we note that the author evaluates the “financial activity” block on the basis of two indicators: return on investment and added value of the company.
The analysis of the sources of scientific literature allows us to conclude that efficiency correlates with the purpose of the enterprise. In this regard, the effectiveness of the financial strategy must be compared with the degree of maximization of the market value of the corporation, i.e. with the dynamics of the "market value".
INTRODUCTION
A financial strategy is needed to achieve the company's goals. When developing it, various options are possible, but for any of them it will be necessary to determine the planning period, outline the main financial goals and ways to achieve them. Equally important is the control over the implementation of the strategy, which allows evaluating the effectiveness of the company's activities, identifying deviations from the planned result and adjusting the strategy for subsequent periods:
- management of current assets and accounts payable;
-management of borrowed funds;
- management of current costs, sales of products and profits;
The financial strategy is a master plan of action to provide the enterprise with funds and manage them.
The financial strategy of any enterprise includes the following elements:
-analysis and assessment of the financial and economic condition of the company;
-development of accounting and tax policies;
-main capital management and depreciation policy;
-dividend and investment policy;
-assessment of the company's achievements and its market value.
Financial strategy means a set of principles and rules that determine the company's financial flows, the boundaries of financial risks, as well as financial goals formulated in a certain set of indicators and rules for their formation.
The financial strategy is closely related to the company's development strategy.
Since the goal of any business is profit, any strategy should be aimed at financial success. Any actions and strategies used in the enterprise must lead to changes in the financial component, otherwise these actions do not make sense. Finance is a service function and the financial strategy will largely depend on the company's marketing strategy.
Usually, strategies begin to be developed when the external conditions for doing business change dramatically, or when the number of internal contradictions and inconsistencies in business processes leads to the realization of the need for qualitative changes. The development of a company's financial strategy includes several main stages. First of all, it is necessary to determine the period of validity of the strategy, the goals of financial activity, to form financial policy and detail financial performance by strategy implementation periods.
The presence of a financial strategy has a positive effect on the performance of the enterprise ... Owners make it clear what they want, and managers - what they can. The number of financial conflicts is reduced, and the financial result is increased.
So, if a company has a financial strategy, it certainly becomes more manageable for management and transparent for owners, more flexible in responding to changes in the business environment and internal processes.
The concept of financial strategy, and its role in the development of the enterprise
When developing a financial strategy, it is necessary to take into account the dynamics of macroeconomic processes, trends in the development of domestic financial markets, and the possibilities for diversifying the activities of an enterprise.
financial strategy,main task which is to achieve full self-sufficiency and independence of the enterprise, is based on certain principles of organization and includes the following:
- current and long-term financial planning, which determines for the future all the receipts of the enterprise's funds and the main directions of their spending;
- centralization of financial resources, ensuring the flexibility of financial resources, their concentration in the main areas of production and economic activity;
- the formation of financial reserves that ensure the stable operation of the enterprise in the face of possible fluctuations in market conditions;
- unconditional fulfillment of financial obligations to partners;
- development of the accounting, financial and depreciation policy of the enterprise;
- organization and maintenance of financial accounting of the enterprise and business segments on the basis of existing standards;
- preparation of financial statements for the enterprise and business segments in accordance with applicable rules and regulations in compliance with the requirements of standards;
- financial analysis of the activity of the enterprise and its segments (priority economic and geographical segments, other segments in the composition of unallocated items);
- financial control of the enterprise and all its segments.
Covering all forms of financial activity of the enterprise, namely: optimization of the main and working capital, the formation and distribution of profits, monetary calculations and investment policy, financial strategy explores the objective economic laws of market relations, develops forms and methods of survival and development under new conditions.
The financial strategy includes the methods and practice of forming financial resources, their planning and ensuring the financial stability of the enterprise. The financial strategy provides for the definition of long-term goals of financial activity and the choice of the most effective ways to achieve them. The goals of the financial strategy should be subordinated to the general strategy of economic development and aimed at maximizing profits and the market value of the enterprise.
In the process of developing a financial strategy, special attention is paid to the production of competitive products, the mobilization of internal resources, the maximum reduction in the cost of production, the formation and distribution of profits, the efficient use of capital, etc.
Consideration of risk factors is of great importance for the formation of a financial strategy. The financial strategy is developed taking into account the risk of non-payments, inflationary fluctuations, and the financial market.
An economic development strategy is a set of main goals and the main means of achieving them. Strategic planning is a unified way of predicting future opportunities, helping to clarify the most appropriate course of action. An analysis of the current values of the parameters and their forecast make it possible to formulate strategic focus - a priority area on which it is necessary to concentrate attention and resources. The scope of the enterprise's priorities should be limited, since the simultaneous implementation of several strategic goals is really impossible..
Taking into account the risk factors and the uncertainty of the development of the external environment, it is almost impossible to choose a single development strategy.
The complexity of developing a strategy is of great importance, since each alternative option provides for an analysis of all issues of its financial, resource and organizational security without exception, the definition and coordination of time and quantitative parameters. Allocation of resources to achieve only a specific goal guarantees the stability of the implementation of the strategy, although it limits the possibility of maneuvering.
A financial strategy is a general plan of action for an enterprise, covering the formation of finances and their planning to ensure the financial stability of the enterprise and includes the following:
- planning, accounting, analysis and control of the financial condition;
- optimization of fixed and working capital;
- distribution of profits.
The financial strategy of the enterprise provides:
- formation and effective use of financial resources;
- identification of the most effective areas of investment and concentration of financial resources in these areas;
- compliance of financial actions with the economic condition and material capabilities of the enterprise;
-determination of the main threat from competitors, the correct choice of directions of financial actions and maneuvering to achieve an advantage over competitors;
- Creation and preparation of strategic reserves;
- ranking and phased achievement of goals.
Tasks of the financial strategy:
-determination of ways of successful use of financial opportunities;
-determination of prospective financial relationships of the enterprise with third parties
-financial support for operating and investment activities;
- study of economic and financial opportunities of potential competitors, development and implementation of measures to ensure financial stability.
The formation and implementation of a financial strategy as the basis for financial planning of an enterprise is based on the use of tools:
- financial management - financial analysis, budgeting, financial control;
- financial services market - factoring, insurance, leasing.
Financial planning is the main form of realization of the main goals of the enterprise. Long-term planning is an important part of the financial strategy of an enterprise and includes the development and forecasting of its financial activities.
The development of a financial strategy is part of the overall strategy for economic development, which is why it must be consistent with its goals and directions. In turn, the financial strategy has a significant impact on the overall economic strategy of the enterprise, since a change in the situation at the macro level and in the financial market is the reason for adjusting not only the financial, but also the general strategy. enterprise development.
stages of financial strategy development
The development of the financial strategy of the enterprise is based on the principles of the new management system of strategic management. The main of these principles that ensure the preparation and adoption of strategic financial decisions in the process of developing the financial strategy of an enterprise include:
Consideration of the enterprise as an open socio-economic system capable of self-organization. This principle of strategic management lies in the fact that when developing a financial strategy, an enterprise is considered as a certain system, completely open for active interaction with environmental factors. In the process of such interaction, the enterprise has the property of acquiring the appropriate spatial, temporal or functional structure without specific external influence in a market-type economy, which is considered as its ability to self-organize. The openness of the enterprise as a socio-economic system and its ability to self-organize make it possible to provide a qualitatively different level of formation of its financial strategy.
Accounting for the basic strategies of the enterprise's operating activities. As part of the overall strategy for the economic development of the enterprise, which primarily ensures the development of operating activities, the financial strategy is subordinate to it. Therefore, it must be consistent with the strategic goals and directions of the enterprise's operating activities. The financial strategy is considered as one of the main factors for ensuring the effective development of the enterprise in accordance with the corporate strategy chosen by it.
However, financial strategy itself has a significant impact on the formation of the strategic development of the operating activities of the enterprise. This is due to the fact that the main goals of the operational strategy - ensuring high rates of product sales, growth in operating profit and increasing the competitive position of the enterprise are associated with the development trends of the relevant product market (consumer or production factors). If the trends in the development of commodity and financial markets (in those segments where the company operates) do not coincide, a situation may arise when the strategic goals for the development of the company's operating activities cannot be implemented due to financial constraints. In this case, the operating strategy of the enterprise is adjusted accordingly.
The whole variety of operating strategies, the implementation of which is designed to ensure the financial activities of the enterprise, can be reduced to the following basic types:
Limited (or concentrated) growth. This type of operating strategy is used by enterprises with a stable product range and production technologies that are not easily affected by technological change. The choice of such a strategy is possible in conditions of relatively weak fluctuations in the commodity market and a stable competitive position of the enterprise. The main types of this basic strategy are: the strategy of strengthening the competitive position; market expansion strategy; product improvement strategy. Accordingly, the financial strategy of the enterprise in these conditions is aimed primarily at the effective provision of reproduction processes and the growth of assets, providing a limited increase in production and sales. Strategic changes financial activities in this case are reduced to a minimum.
Accelerated (integrated or differentiated) growth. This type of operational strategy is chosen, as a rule, by enterprises that are in the early stages of their life cycle, as well as in dynamically developing industries under the influence of technological progress. The main types of this basic strategy are: vertical integration strategy; reverse integration strategy; horizontal diversification strategy; conglomerate diversification strategy.
Reducing (or shrinking). This operating strategy is most often chosen by enterprises in the last stages of their life cycle, as well as in the stage of financial crisis. It is based on the principle of "cutting off the excess", which provides for a reduction in the volume and range of products, withdrawal from certain market segments, etc. The main types of this basic strategy are: structure reduction strategy; cost reduction strategy; "harvest" strategy; elimination strategy. The financial strategy of the enterprise in these conditions is designed to ensure effective disinvestment and high flexibility in the use of released capital in order to ensure further financial stabilization.
Combination (or combination). Such an operating strategy of an enterprise integrates the considered various types of private strategies of individual strategic business zones or strategic business units. This strategy is typical for the largest enterprises (organizations) with a wide industry and regional diversification of operations.
Primary focus on the entrepreneurial style of strategic financial management. The financial management of an enterprise in a strategic perspective is characterized by an incremental or entrepreneurial style.
The basis of the incremental style of strategic financial management is the setting of strategic goals based on the achieved level of financial activity with minimizing the alternativeness of strategic financial decisions. Fundamental changes in the directions and forms of financial activity are carried out only as a response to changes in the operating strategy of the enterprise. This style of strategic financial management is usually typical for enterprises that have reached the maturity stage of their life cycle.
The basis of the entrepreneurial style of strategic financial management is the active search for effective management decisions in all areas and forms of financial activity. This style of financial management is associated with a constant transformation of the directions, forms and methods of financial activities all the way to achieving the set strategic goals, taking into account changing environmental factors.
Identification of dominant areas of strategic financial development. This principle makes it possible to identify the priority areas of the financial activity of the enterprise, ensuring the successful implementation of its main target function - the increase in the market value of the enterprise in the long term.
Strategy for the formation of financial resources of the enterprise. The goals, objectives and main strategic decisions of this dominant financial strategy should be aimed at financial support for the implementation of the corporate strategy of the enterprise and, accordingly, subordinate to it.
The strategy of distribution of financial resources of the enterprise. The parameters of the strategic set of this dominant financial strategy should, on the one hand, be aimed at financial support for the implementation of individual functional strategies and strategies of economic units, and on the other hand, form the basis for the formation of directions for the investment activity of an enterprise in a strategic perspective.
Strategy for ensuring the financial security of the enterprise. The goals, objectives and most important strategic decisions of this dominant financial strategy should be aimed at the formation and support of the main parameters of the financial balance of the enterprise in the process of its strategic development.
Strategy for improving the quality of financial management of the enterprise. The parameters of the strategic set of this dominant financial strategy are developed by the financial services of the enterprise and are included as an independent block in the corporate and individual functional strategies of the enterprise.
Ensuring the flexibility of the financial strategy. The future development of the financial activity of the enterprise is always characterized by significant uncertainty. Therefore, it is practically impossible to keep the developed financial strategy of the enterprise unchanged at all stages of the process of its implementation. Strategic flexibility is the potential ability of an enterprise to quickly adjust or develop new strategic financial decisions in the face of changing external or internal conditions for the implementation of financial activities. It is achieved with such intra-organizational coordination of financial activities, in which financial resources can be easily transferred from one strategic business area or economic unit to another. The ability to timely maneuver financial resources is achieved if the enterprise has a sufficient amount of them in the form of insurance reserves and integrated management of these reserves. Besides , important role a sufficient level of liquidity of assets and investments of the enterprise plays a role in ensuring the flexibility of the financial strategy. To this end, an enterprise may sometimes deliberately maintain certain types of financial investments with low returns but high levels of liquidity in order to provide the necessary strategic flexibility due to the ability to quickly reinvest capital.
6. Providing an alternative strategic financial choice. Strategic financial decisions should be based on an active search for alternative options for the directions, forms and methods of financial activities, the selection of the best of them, the construction of a general financial strategy on this basis and the formation of mechanisms for its effective implementation. Alternative is the most important distinguishing feature of the entire system of strategic enterprise management and is associated with all the main elements of the strategic financial set - financial goals, financial policy on certain aspects of financial activity, sources of formation of financial resources, style and mentality of financial management, etc.
7. Ensuring continuous use of the results of technological progress in financial activities. When forming a financial strategy, it should be borne in mind that financial activity is the main mechanism for ensuring the introduction of technological innovations that ensure the growth of the competitive position of an enterprise in the market. Therefore, the implementation of the general goals of the strategic development of an enterprise largely depends on how its financial strategy reflects the results of technological progress and is adapted to the rapid use of its new results.
8. Accounting for the level of financial risk in the process of making strategic financial decisions. Almost all major financial decisions taken in the process of forming a financial strategy, to one degree or another, change the level of financial risk. First of all, this is due to the choice of directions and forms of financial activity, the formation of financial resources, the introduction of new organizational structures for managing financial activities. The level of financial risk increases especially strongly during periods of interest rate fluctuations and inflation growth. Due to the different mentality of financial managers in relation to the level of acceptable financial risk (their risk preferences) at each enterprise in the process of developing a financial strategy this parameter must be set differentially.
9. Orientation to the professional apparatus of financial managers in the process of implementing the financial strategy. Whatever specialists are involved in the development of individual parameters of the financial strategy of the enterprise, its implementation should be ensured by trained specialists - financial managers. These managers must be familiar with the basic principles of strategic management, the mechanism for managing certain aspects of financial activity, and master the methods of strategic financial controlling.
Providing the developed financial strategy of the enterprise with the appropriate organizational structure for managing financial activities and organizational culture. The most important condition for the effective implementation of the financial strategy is the corresponding changes in the organizational structure of management and organizational culture. The envisaged strategic changes in this area should be an integral part of the parameters of the financial strategy that ensure its feasibility.
The development of the main elements of a strategic set in the field of financial activity of an enterprise is based on the results of a strategic financial analysis.
The final product of strategic financial analysis is a model of the strategic financial position of an enterprise, which comprehensively and comprehensively characterizes the prerequisites and opportunities for its financial development in the context of each of the strategic dominant areas of financial activity.
Strategic planning is implemented sequentially in stages:
Organization mission statement
Goal setting
Assessment and analysis of the external environment
Choice
strategies
Implementation of the strategy and subsequent evaluation of results
Analysis of strategic alternatives
Management review of the organization.
Organizational mission statement and goal setting. The mission of the organization is the main common goal, a clearly expressed reason for its existence.
The objectives of the enterprise must be specific and measurable. They are usually installed for long or short periods of time. A long-term goal has a planning horizon of five or more years. A short-term goal usually represents one of the plans to be completed within a year. Medium-term goals have a planning horizon of one to five years. Long-term goals are formulated first. Then medium and short-term goals are set, necessary to ensure long-term goals. Usually, the closer the planning horizon of the goal, the narrower the scope of the tasks set. For example, a long-term productivity goal might be: increase overall productivity by 25% in five years. Then the medium-term goal is to increase productivity by 10% in two years. The goal set must be achievable. Setting a goal that exceeds the capacity of the organization can be disastrous. If the goals are unattainable, the desire of employees to succeed will be blocked and their motivation will weaken - unattainable goals will disorganize the staff.
Assessment and analysis of the external environment is the process by which strategic planners evaluate factors external to the organization in order to identify opportunities and threats for the firm. Evaluate according to three parameters: 1) changes that affect different aspects of the current strategy. For example, rising fuel prices create problems for airlines, so they must continually assess fuel price developments; 2) factors that pose a threat to the current strategy of the firm. For example, if there are competitors, you need to control their activities. ; 3) factors that determine new opportunities to achieve the goals of the enterprise.
Threats and opportunities can generally be classified into seven areas: economics, politics, markets, technology, competition, international standing, and social behavior.
Environmental factors:
Economic forces.
political factors.
market factors.
Technological factors.
international factors.
Competition factors.
Management review of the organization. A management survey is a methodical assessment of the functional areas of an organization, designed to identify its strategic strengths and weaknesses. In the simplest case, five functions are recommended to be included in the survey - marketing, finance and accounting, production, human resources, and culture and image of the organization.
At the present stage of economic development, the environment for the functioning of enterprises has changed significantly. They are under high competitive pressure from both domestic and especially foreign manufacturers with greater financial and production capabilities. There are also changes in the ratio and mobility of factors of production, including capital, intellectual, human and natural resources. In addition, for activities industrial enterprises environmental factors that have an indirect impact also influence: political, economic, social, legal, technical and technological, and others. This reinforces the state of uncertainty when making decisions. management decisions in all areas of the enterprise, including financial. In this regard, company leaders need to promptly and quickly respond to external changes, as well as purposefully use the existing internal capabilities, which requires competencies in the field of strategic management. Each company, accordingly, must develop a strategy that is adequate to the prevailing conditions.
From our point of view, strategy is a set of strategic actions and decisions of the company to changes in environmental factors. A strategy is necessary to respond to changes in external factors and adapt the company's internal capabilities to the requirements of the changing environment of its functioning in order to ensure competitiveness.
Strategic management of a corporate type enterprise can be carried out at the level of the entire company, business units, as well as by functional areas of activity (Fig. 1).

Rice. 1. Classification of strategies of a corporate type company
The corporate level is highest level organization, which determines the overall corporate strategy. Corporate type companies are usually a business portfolio or aggregate strategic business units(SBE). The business portfolio is coordinated through a corporate strategy that includes a long-term vision, common goals, philosophy and culture. A long-term vision is an idea of the future of a corporation, its ideal image. It defines the direction of the organization and shows what it should strive for. Corporate goals are strategic planned indicators that the organization as a whole must achieve in order to realize its long-term vision (profit generation, sales growth, market share increase, product quality improvement, employee welfare growth, etc.). A corporation may also have its own philosophy and culture. Philosophy establishes the values and principles of doing business accepted in the organization, and corporate culture determines the general socio-psychological attitudes and norms of behavior shared by all employees.
The business unit strategy defines how the SBU will help implement the company-wide strategy. The business unit strategy consists of three components: mission, goals and competencies. The SBU's mission is a statement that defines the markets in which it will compete, as well as the range of products with which it will enter the market. SBU goals are planned indicators that a business unit will strive to achieve in order to fulfill its mission (the degree of satisfaction of consumer needs, the quality of business processes and products, the level of innovation, etc.). The implementation of the mission and goals of the SBU depend on its competence. At the same time, the competence of a business unit means its special abilities, due to the quality of all types of resources, technologies, functional units.
On the basis of strategic guidelines at the corporate and business levels, the setting and implementation of functional goals are carried out. Functional goals are a development of the goals defined at the corporate and business unit level. Accordingly, in the strategic management system, along with the corporate strategy and strategies of business units, functional strategies are also developed, formed by the main activities of the company and associated with the two strategies discussed above. The purpose of functional strategies is to ensure the implementation of the strategies of business units and the company as a whole. The financial strategy of an enterprise, as shown in Figure 1, belongs to the category of functional strategies.
The financial strategy of a corporate type enterprise is one of the functional strategies of the company and represents the direction of strategic actions in the field of finance related to the mobilization of financial resources from all possible sources and their effective use. The financial strategy is aimed at mobilizing the financial resources of the organization and their rational distribution and use, that is, it forms the prerequisites for the implementation of functional strategies, business unit strategies and corporate strategy. At the same time, the successful implementation of these strategies, in turn, leads to an increase in income, profits of the organization, an increase in its assets and the market value of the company. The financial strategy allows the enterprise to adapt in a timely manner to changes in the factors of the external and internal environment, to use financial and investment opportunities for economic growth.
The company can develop alternative options for financial strategies and choose the most appropriate option depending on the operating conditions of the corporation, the financial capabilities of its development and the level of competitiveness. Figure 2 shows the classification of financial strategies developed by us.


Rice. 2. Classification of financial strategies of an industrial enterprise
From our point of view, this classification takes into account, firstly, the sources of financing of the corporation's activities. A corporate-type enterprise may use its own financial resources generated by issuing shares, net profit and targeted financing from budgetary and non-budgetary funds. Borrowed capital can be represented by long-term and short-term liabilities, such as credit resources, accounts payable, estimated liabilities, deferred income.
Secondly, depending on the external conditions of functioning, the enterprise can develop a growth strategy. It requires significant costs and is associated with a high risk that the investments made may not give the expected effect, however, favorable external conditions and competent mobilization of financial resources can contribute to the growth of the market value of the enterprise and increase the efficiency of its activities.
The choice by the corporation of one or another strategy of strengthening competitive advantage depends on its strengths and weaknesses, as well as on the presence and strength of competitors. The strategy of improving the quality of products and reducing costs will allow the company to effectively distribute and use all available hidden opportunities and reserves. It will increase the profitability of production and competitive positions. Companies pursuing an innovation strategy should focus on creating new types of products, modernizing the product portfolio and production capacity, the introduction of new technologies, the improvement of methods of organizing production. The implementation of this strategy can ensure the growth of sales and profits, however, it is associated with high costs of financial resources and increased financial risks. An enterprise that implements a strategy of focusing on a selected market segment is able to pursue a narrow strategic goal with greater efficiency than competitors operating in a wider area.
The Prudent Business Strategy is designed to maintain the company's current business growth rates by balancing the parameters of limited operating growth and minimizing financial risks. The anti-crisis financial strategy should ensure the improvement of the financial situation at the enterprise during the crisis periods of its activity. When developing it, it is necessary to make decisions related to reducing the volume of production and sales of products, getting rid of non-core assets, unprofitable types of products, and strict control of financial flows. It is also necessary to control the liquidity, solvency, financial stability of the corporation to prevent bankruptcy.
Thus, the financial strategy of a corporate type enterprise, as one of its functional strategies, is aimed at the formation, distribution and efficient use of financial resources. Depending on the external conditions of functioning, the corporation can implement various options for financial strategies. The types of considered financial strategies are classified according to the following criteria: depending on the sources of financing of the enterprise's activities and on the prospects for business development.
Literature:
1. Ivanov, I. V. Financial management: cost approach: Tutorial/ I. V. Ivanov, V. V. Baranov. - M. : Alpina Business Books, 2008.
2. Yarygina, N.S. Theoretical approaches to the classification of financial strategies of the company / N.S. Yarygin. - Collection of materials of the IV International scientific and practical conference "The quality of economic development: global and local aspects": In 3 volumes, Volume 3: Modern economy. - Dnepropetrovsk: Bila K. O., 2012. - 100 p.


